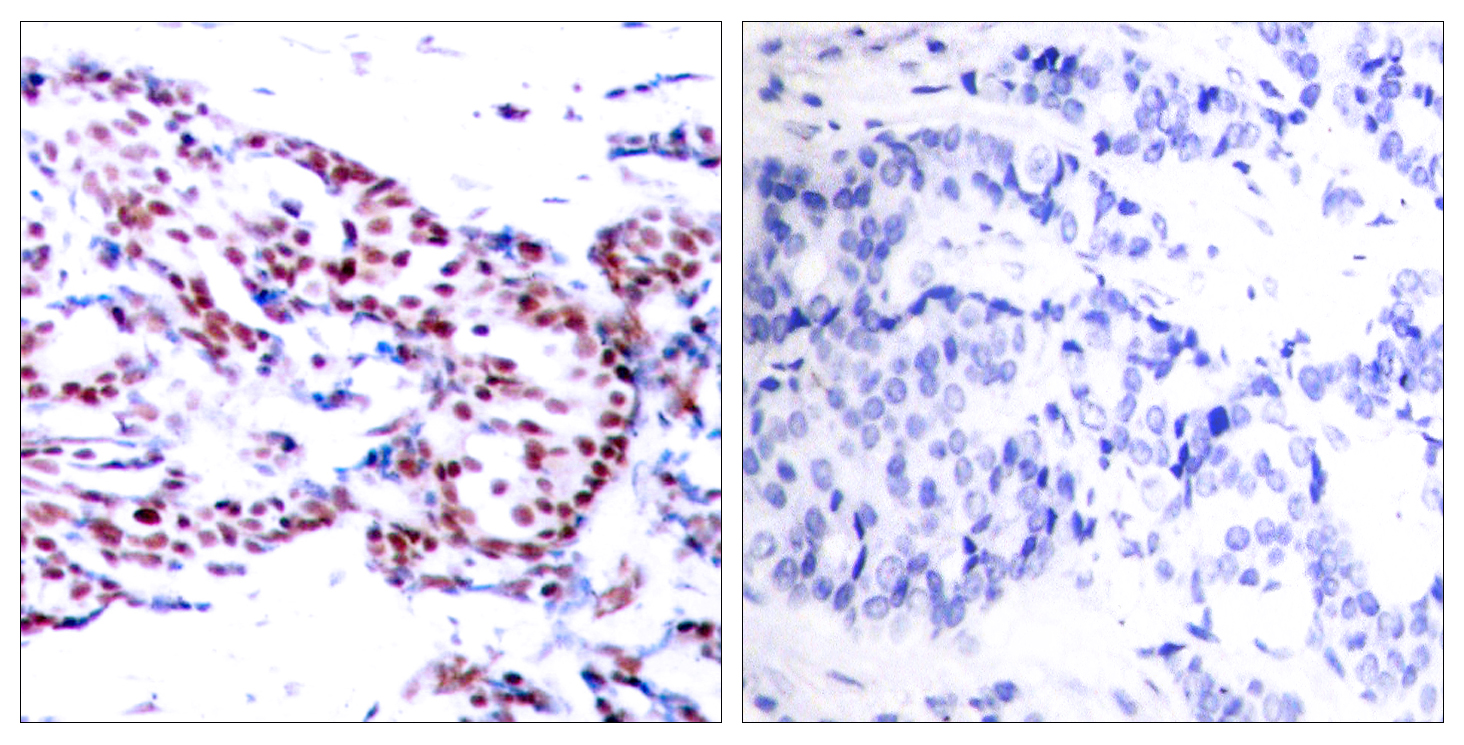
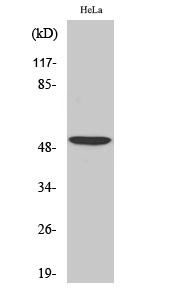
Total ATF-2 Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA3028C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Gene Name:
- ATF2
- Human Gene Id:
- 1386
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P15336
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P16951
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q00969
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-2 (cAMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-2) (Activating transcription factor 2) (Cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein 2) (CREB-2) (cAMP-responsive element-binding protein 2) (HB16) (cAMP response element-binding protein CRE-BP1)
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- caution:It is uncertain whether Met-1 or Met-19 is the initiator.,function:Transcriptional activator, probably constitutive, which binds to the cAMP-responsive element (CRE) (consensus: 5'-GTGACGT[AC][AG]-3'), a sequence present in many viral and cellular promoters. Interaction with JUN redirects JUN to bind to CRES preferentially over the 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate response elements (TRES) as part of an ATF2-c-Jun complex.,PTM:Phosphorylation of Thr-69 and Thr-71 by MAPK14 causes increased transcriptional activity. Also phosphorylated and activated by JNK.,similarity:Belongs to the bZIP family.,similarity:Belongs to the bZIP family. ATF subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 bZIP domain.,similarity:Contains 1 C2H2-type zinc finger.,subunit:Binds DNA as a dimer and can form a homodimer in the absence of DNA. Can form a heterodimer with JUN. Interacts with SMAD3 and SMAD4. Binds through its N-terminal region to UTF1 which acts as a coactivator of ATF2 transcriptional activity.,tissue specificity:Abundant expression seen in the brain.,
- Function:
- transcription, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription, regulation of RNA metabolic process,
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Mitochondrion outer membrane. Shuttles between the cytoplasm and the nucleus and heterodimerization with JUN is essential for the nuclear localization. Localization to the cytoplasm is observed under conditions of cellular stress and in disease states. Localizes at the mitochondrial outer membrane in response to genotoxic stress. Phosphorylation at Thr-52 is required for its nuclear localization and negatively regulates its mitochondrial localization. Co-localizes with the MRN complex in the IR-induced foci (IRIF).
- Expression:
- Ubiquitously expressed, with more abundant expression in the brain.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs