Fibrinogen γ Monoclonal Antibody
- 货号:YM0270
- 应用:WB;IHC;IF;FCM;ELISA
- 种属:Human
- 简介:
- >>Complement and coagulation cascades;>>Platelet activation;>>Neutrophil extracellular trap formation;>>Staphylococcus aureus infection;>>Coronavirus disease - COVID-19
- 蛋白名称:
- Fibrinogen gamma chain
- 免疫原:
- Purified recombinant fragment of human Fibrinogen γ expressed in E. Coli.
- 特异性:
- Fibrinogen γ Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Fibrinogen γ protein.
- 组成:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- 稀释:
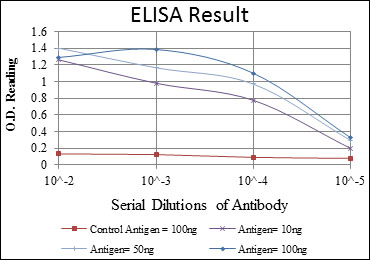
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:200 - 1:1000. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. Flow cytometry: 1:200 - 1:400. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- 纯化工艺:
- Affinity purification
- 储存:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- 其他名称:
- FGG;Fibrinogen gamma chain
- 背景:
- The protein encoded by this gene is the gamma component of fibrinogen, a blood-borne glycoprotein comprised of three pairs of nonidentical polypeptide chains. Following vascular injury, fibrinogen is cleaved by thrombin to form fibrin which is the most abundant component of blood clots. In addition, various cleavage products of fibrinogen and fibrin regulate cell adhesion and spreading, display vasoconstrictor and chemotactic activities, and are mitogens for several cell types. Mutations in this gene lead to several disorders, including dysfibrinogenemia, hypofibrinogenemia and thrombophilia. Alternative splicing results in transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2015],
- 功能:
- disease:Defects in FGG are a cause of congenital afibrinogenemia [MIM:202400]. It is a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by complete absence of detectable fibrinogen.,disease:Defects in FGG are a cause of thrombophilia.,domain:A long coiled coil structure formed by 3 polypeptide chains connects the central nodule to the C-terminal domains (distal nodules). The long C-terminal ends of the alpha chains fold back, contributing a fourth strand to the coiled coil structure.,function:Fibrinogen has a double function: yielding monomers that polymerize into fibrin and acting as a cofactor in platelet aggregation.,miscellaneous:The gamma-chain carries the main binding site for the platelet receptor.,online information:Fibrinogen entry,PTM:Conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin is triggered by thrombin, which cleaves fibrinopeptides A and B from alpha and beta chains, and thus exposes th
- 组织表达:
- Detected in blood plasma (at protein level).

- Western Blot analysis using Fibrinogen γ Monoclonal Antibody against recombinant protein.
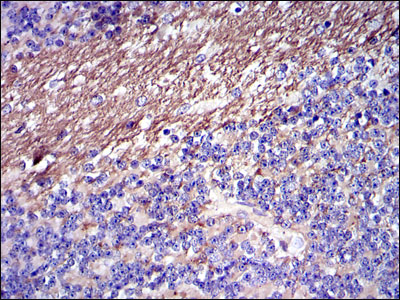
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded cerebellum tissues with DAB staining using Fibrinogen γ Monoclonal Antibody.
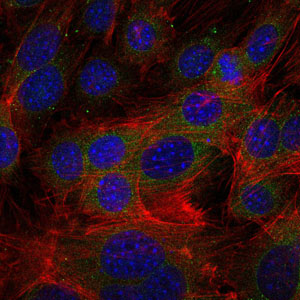
- Immunofluorescence analysis of 3T3-L1 cells using Fibrinogen γ Monoclonal Antibody (green). Blue: DRAQ5 fluorescent DNA dye. Red: Actin filaments have been labeled with Alexa Fluor-555 phalloidin.
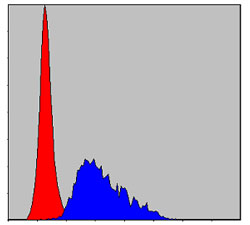
- Flow cytometric analysis of HepG2 cells using Fibrinogen γ Monoclonal Antibody (blue) and negative control (red).