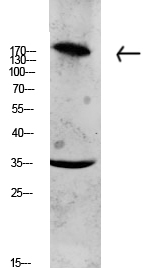
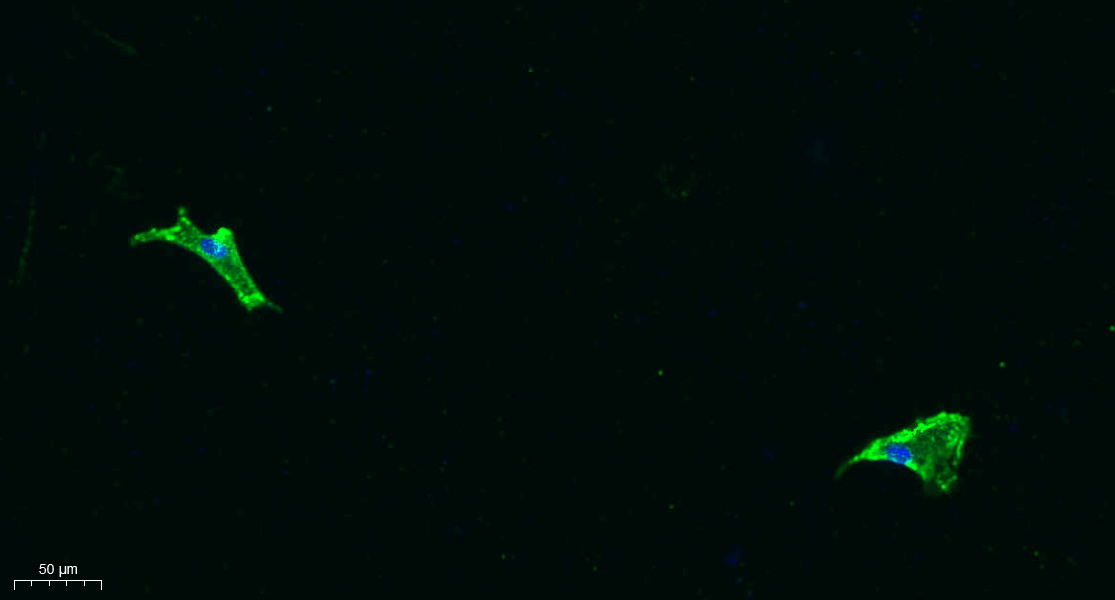
Total Collagen XI α1 Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- 货号:KA4049C
- 应用:ELISA
- 种属:Human;Mouse
- 基因名称:
- COL11A1
- Human Gene Id:
- 1301
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P12107
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q61245
- 储存:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- 其他名称:
- Collagen alpha-1(XI) chain
- 检测方法:
- Colorimetric
- 背景:
- alternative products:Additional isoforms seem to exist. There is alternative usage of exon IIA or exon IIB. Transcripts containing exon IIA or IIB are present in cartilage, but exon IIB is preferentially utilized in transcripts from tendon,disease:Defects in COL11A1 are the cause of Marshall syndrome [MIM:154780]. It is an autosomal dominant disorder with ocular, orofacial, auditory and skeletal manifestations. It shares several features with Stickler syndrome, such as midfacial hypoplasia, high myopia, and sensorineural-hearing deficit.,disease:Defects in COL11A1 are the cause of Stickler syndrome type 2 (STL2) [MIM:604841]; also known as Stickler syndrome vitreous type 2. STL2 is an autosomal dominant form of Stickler syndrome, an inherited disorder that associates ocular signs with more or less complete forms of Pierre Robin sequence, bone disorders and sensorineural deafness. Ocular disorders may include juvenile cataract, myopia, strabismus, vitreoretinal or chorioretinal degeneration, retinal detachment, and chronic uveitis. Robin sequence includes an opening in the roof of the mouth (a cleft palate), a large tongue (macroglossia), and a small lower jaw (micrognathia). Bones are affected by slight platyspondylisis and large, often defective epiphyses. Juvenile joint laxity is followed by early signs of arthrosis. The degree of hearing loss varies among affected individuals and may become more severe over time. Syndrome expressivity is variable.,function:May play an important role in fibrillogenesis by controlling lateral growth of collagen II fibrils.,PTM:Prolines at the third position of the tripeptide repeating unit (G-X-Y) are hydroxylated in some or all of the chains.,similarity:Belongs to the fibrillar collagen family.,similarity:Contains 1 TSP N-terminal (TSPN) domain.,subunit:Trimers composed of three different chains: alpha 1(XI), alpha 2(XI), and alpha 3(XI). Alpha 3(XI) is a post-translational modification of alpha 1(II). Alpha 1(V) can also be found instead of alpha 3(XI)=1(II).,tissue specificity:Cartilage, placenta and some tumor or virally transformed cell lines. Isoforms using exon IIA or IIB are found in the cartilage while isoforms using only exon IIB are found in the tendon.,
- 功能:
- skeletal system development, cartilage condensation, chondrocyte differentiation, chondrocyte development, heart morphogenesis, proteoglycan metabolic process, cell adhesion, sensory organ development, heart development,muscle organ development, sensory perception, visual perception, sensory perception of sound, glycoprotein metabolic process, detection of external stimulus, detection of abiotic stimulus, response to mechanical stimulus,response to abiotic stimulus, embryonic development ending in birth or egg hatching, striated muscle tissue development, cell-cell adhesion, biological adhesion, extracellular matrix organization, collagen fibril organization, ear morphogenesis, inner ear morphogenesis, chordate embryonic development, extracellular structure organization, ear development, embryonic organ morphogenesis, embryonic organ development, embryonic morphogenesis, embryonic skelet
- 细胞定位:
- Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix .
- 组织表达:
- Cartilage, placenta and some tumor or virally transformed cell lines. Isoforms using exon IIA or IIB are found in the cartilage while isoforms using only exon IIB are found in the tendon.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs