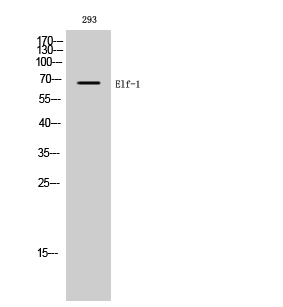
Total Elf-1 Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- 货号:KA3587C
- 应用:ELISA
- 种属:Human
- 其他名称:
- ETS-related transcription factor Elf-1 (E74-like factor 1)
- 背景:
- function:Transcription factor that activates the LYN and BLK promoters. Appears to be required for the T-cell-receptor-mediated trans activation of HIV-2 gene expression. Binds specifically to two purine-rich motifs in the HIV-2 enhancer.,PTM:Phosphorylated upon DNA damage, probably by ATM or ATR.,similarity:Belongs to the ETS family.,similarity:Contains 1 ETS DNA-binding domain.,subunit:Binds to the underphosphorylated form of RB. May interact with other transcription factors in order to regulate specific genes. Interacts with RUNX1.,tissue specificity:In fetal tissue, it is highly expressed in heart, lung liver and kidney, and weakly expressed in brain. In adult, it is highly expressed in pancreas, spleen, thymus and peripheral blood leukocytes, expressed at moderate levels in heart, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscle, kidney, prostate, ovary, small intestine and colon, and weakly expressed in brain and testis.,
- 功能:
- regulation of cytokine production, negative regulation of immune system process, transcription, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, positive regulation of biosynthetic process, negative regulation of signal transduction, positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, positive regulation of gene expression, negative regulation of cell communication, positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process, regulation of transcription,positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process, positive regulation of transcription, positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, regulation of antigen receptor-mediated signaling pathway, regulation of T
- 组织表达:
- In fetal tissues, it is highly expressed in heart, lung liver and kidney, and weakly expressed in brain. In adult, it is highly expressed in pancreas, spleen, thymus and peripheral blood leukocytes, expressed at moderate levels in heart, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscle, kidney, prostate, ovary, small intestine and colon, and weakly expressed in brain and testis.