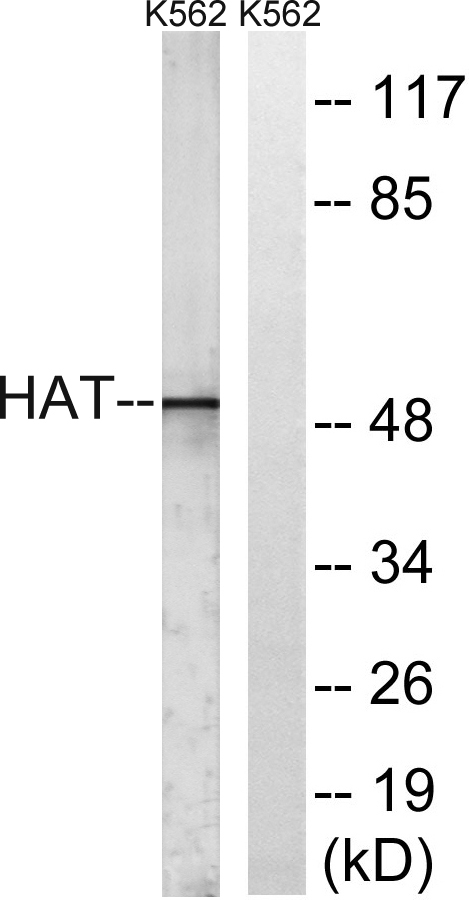
Total HAT1 Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- 货号:KA3406C
- 应用:ELISA
- 种属:Human;Mouse;Rat
- 其他名称:
- Histone acetyltransferase type B catalytic subunit (EC 2.3.1.48) (Histone acetyltransferase 1)
- 背景:
- catalytic activity:Acetyl-CoA + histone = CoA + acetylhistone.,function:May play a role in telomeric silencing. Acetylates soluble but not nucleosomal H4 at 'Lys-5' and 'Lys-12' and acetylates histone H2A at 'Lys-5'. HAT1 has intrinsic substrate specificity that modifies lysine in recognition sequence GXGKXG.,online information:Histone acetyltransferase entry,similarity:Belongs to the HAT1 family.,subcellular location:Nuclear in S-phase cells and cytoplasmic.,subunit:Heteromer of HAT1 and p46/HAT2 subunits.,
- 功能:
- DNA packaging, chromatin organization, chromatin silencing, chromatin silencing at telomere, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, protein amino acid acetylation, internal protein amino acid acetylation, negative regulation of biosynthetic process, negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, negative regulation of gene expression, gene silencing, negative regulation of transcription, chromatin modification, covalent chromatin modification, histone modification, histone acetylation,negative regulation of cellular biosynthetic process, regulation of gene expression, epigenetic, protein amino acid acylation, regulation of transcription, negative regulation of gene expression, epigenetic, negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, negative regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid m
- 细胞定位:
- [Isoform A]: Nucleus matrix . Mitochondrion .; [Isoform B]: Cytoplasm . Nucleus . Nucleus matrix . Nucleus, nucleoplasm . Localization is predominantly nuclear in normal cells. Treatment with hydrogen peroxide or ionizing radiation enhances nuclear localization through redistribution of existing protein. .