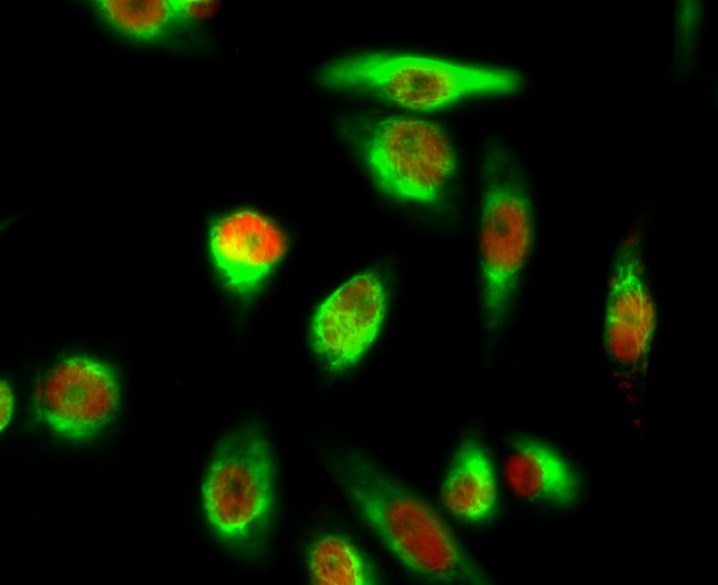
YAP Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT4924
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- YAP
- Fields:
- >>Hippo signaling pathway;>>Hippo signaling pathway - multiple species
- Gene Name:
- YAP1
- Protein Name:
- Yorkie homolog
- Human Gene Id:
- 10413
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P46937
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 22601
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P46938
- Rat Gene Id:
- 363014
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q2EJA0
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human YAP. AA range:281-330
- Specificity:
- YAP Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of YAP protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:5000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- YAP1;YAP65;Yorkie homolog;65 kDa Yes-associated protein;YAP65
- Observed Band(KD):
- 67kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a downstream nuclear effector of the Hippo signaling pathway which is involved in development, growth, repair, and homeostasis. This gene is known to play a role in the development and progression of multiple cancers as a transcriptional regulator of this signaling pathway and may function as a potential target for cancer treatment. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2013],
- Function:
- PTM:Phosphorylated upon DNA damage, probably by ATM or ATR.,similarity:Contains 1 WW domain.,subunit:Binds to the SH3 domain of the YES kinase. Binds to WBP1 and WBP2. Binds, in vitro, through the WW1 domain, to neural isoforms of ENAH that contain the PPSY motif.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm . Nucleus . Both phosphorylation and cell density can regulate its subcellular localization (PubMed:18158288, PubMed:20048001). Phosphorylation sequesters it in the cytoplasm by inhibiting its translocation into the nucleus (PubMed:18158288, PubMed:20048001). At low density, predominantly nuclear and is translocated to the cytoplasm at high density (PubMed:18158288, PubMed:20048001, PubMed:25849865). PTPN14 induces translocation from the nucleus to the cytoplasm (PubMed:22525271). Localized mainly to the nucleus in the early stages of embryo development with expression becoming evident in the cytoplasm at the blastocyst and epiblast stages (By similarity). .
- Expression:
- Increased expression seen in some liver and prostate cancers. Isoforms lacking the transactivation domain found in striatal neurons of patients with Huntington disease (at protein level).
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs