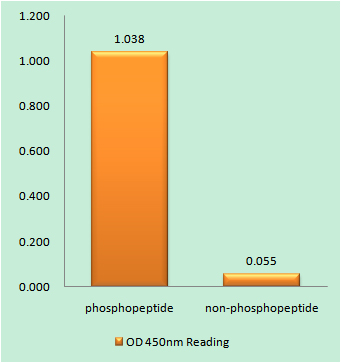
Phospho Calcium Sensing Receptor (T888) Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA1427C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Gene Name:
- CASR
- Human Gene Id:
- 846
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P41180
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q9QY96
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P48442
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- Extracellular calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) (Parathyroid cell calcium-sensing receptor) (PCaR1)
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- disease:Defects in CASR are the cause of autosomal dominant hypoparathyroidism (FIH) [MIM:146200]. FIH is characterized by hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia due to inadequate secretion of parathyroid hormone. Symptoms are seizures, tetany and cramps.,disease:Defects in CASR are the cause of familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia type 1 (FHH) [MIM:145980]; in which the receptor has reduced activity. FHH is characterized by altered calcium homeostasis. Affected individuals exhibit mild or modest hypercalcemia, relative hypocalciuria, and inappropriately normal PTH levels.,disease:Defects in CASR are the cause of neonatal severe primary hyperparathyroidism (NSHPT) [MIM:239200]; in which the receptor has reduced activity. NSHPT is a rare autosomal recessive life-threatening disorder characterized by very high serum calcium concentrations, skeletal demineralization, and parathyroid hyperplasia. In some instances NSHPT has been demonstrated to be the homozygous form of FHH.,function:Senses changes in the extracellular concentration of calcium ions. The activity of this receptor is mediated by a G-protein that activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system.,PTM:N-glycosylated.,PTM:Ubiquitinated by RNF19A; which induces proteasomal degradation.,similarity:Belongs to the G-protein coupled receptor 3 family.,subunit:Interacts with VCP and RNF19A.,tissue specificity:Found in kidney, but not in brain, lung, liver, heart, skeletal muscle, or placenta.,
- Function:
- skeletal system development, ossification, detection of calcium ion, cellular ion homeostasis, cellular calcium ion homeostasis, cellular metal ion homeostasis, cell surface receptor linked signal transduction, G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway, intracellular signaling cascade, behavior, chemosensory behavior, detection of chemical stimulus, response to inorganic substance, response to metal ion, regulation of metal ion transport, calcium-mediated signaling, cellular homeostasis, second-messenger-mediated signaling, cellular cation homeostasis, cellular di-, tri-valent inorganic cation homeostasis, positive regulation of ATPase activity, homeostatic process, positive regulation of catalytic activity, regulation of ion transport, regulation of ATPase activity, positive regulation of molecular function, chemical homeostasis, ion homeostasis, regulation of hydrolase activ
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein .
- Expression:
- Expressed in the temporal lobe, frontal lobe, parietal lobe, hippocampus, and cerebellum. Also found in kidney, lung, liver, heart, skeletal muscle, placenta.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs