MRTF-A Polyclonal Antibody
- 货号:YT2895
- 应用:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- 种属:Human;Mouse
- 蛋白名称:
- MKL/myocardin-like protein 1
- 免疫原:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human MKL1. AA range:10-59
- 特异性:
- MRTF-A Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of MRTF-A protein.
- 组成:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- 来源:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- 稀释:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:5000.. IF 1:50-200
- 纯化工艺:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- 储存:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- 其他名称:
- MKL1;KIAA1438;MAL;MKL/myocardin-like protein 1;Megakaryoblastic leukemia 1 protein;Megakaryocytic acute leukemia protein;Myocardin-related transcription factor A;MRTF-A
- 背景:
- The protein encoded by this gene interacts with the transcription factor myocardin, a key regulator of smooth muscle cell differentiation. The encoded protein is predominantly nuclear and may help transduce signals from the cytoskeleton to the nucleus. This gene is involved in a specific translocation event that creates a fusion of this gene and the RNA-binding motif protein-15 gene. This translocation has been associated with acute megakaryocytic leukemia. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2013],
- 功能:
- disease:A chromosomal aberration involving MKL1 may be a cause of acute megakaryoblastic leukemia. Translocation t(1;22)(p13;q13) with RBM15. Although both reciprocal fusion transcripts are detected in acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL, FAB-M7), the RBM15-MKL1 chimeric protein has all the putative functional domains encoded by each gene and is the candidate oncogene.,domain:The N-terminal region is required for nuclear localization and the C-terminal region mediates transcriptional activity.,function:Transcriptional factor which uses the canonical single or multiple CArG boxes DNA sequence. Acts as a cofactor of serum response factor (SRF) and has the potential to modulate SRF-target genes. Suppresses TNF-induced cell death by inhibiting activation of caspases; its transcriptional activity is indispensable for the antiapoptotic function. It may up-regulate antiapoptotic molecules, wh
- 细胞定位:
- Cytoplasm . Nucleus . Subcellular location is tightly regulated by actin both in cytoplasm and nucleus: high levels of G-actin in the nucleus observed during serum deprivation lead to low levels of nuclear MRTFA, while reduced levels of nuclear G-actin result in accumulation of MRTFA in the nucleus (By similarity). G-actin-binding in the cytoplasm inhibits nuclear import by masking the nuclear localization signal (NLS) (By similarity). In contrast, binding to nuclear globular actin (G-actin) promotes nuclear export to the cytoplasm (By similarity). Nuclear localization is regulated by MICAL2, which mediates depolymerization of nuclear actin, which decreases nuclear G-actin pool, thereby promoting retention of MRTFA in the nucleus and subsequent formation of an active complex with SRF (PubM
- 组织表达:
- Ubiquitously expressed, has been detected in lung, placenta, small intestine, liver, kidney, spleen, thymus, colon, muscle, heart and brain (PubMed:11344311). Expressed in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (at protein level) (PubMed:26224645).
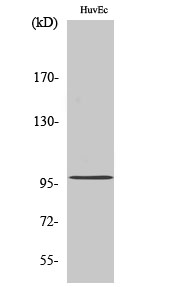
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using MRTF-A Polyclonal Antibody
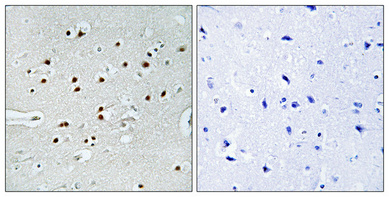
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Human brain. Antibody was diluted at 1:100(4° overnight). High-pressure and temperature Tris-EDTA,pH8.0 was used for antigen retrieval. Negetive contrl (right) obtaned from antibody was pre-absorbed by immunogen peptide.
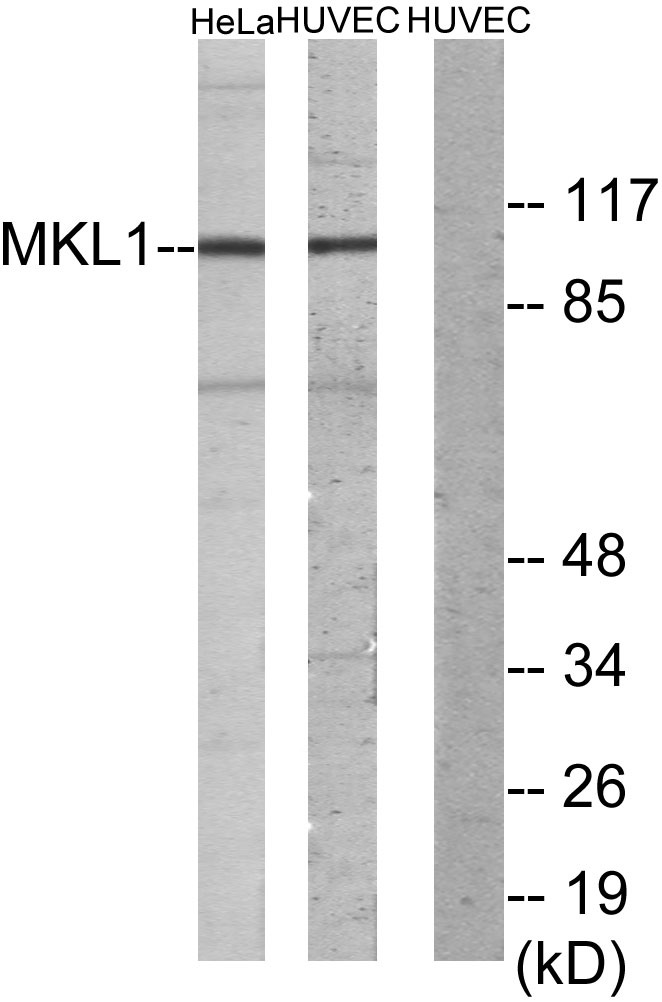
- Western blot analysis of lysates from HUVEC and HeLa cells, using MKL1 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.






