Laminin α-3 Polyclonal Antibody
- 货号:YT2525
- 应用:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- 种属:Human;Mouse;Rat
- 简介:
- >>PI3K-Akt signaling pathway;>>Focal adhesion;>>ECM-receptor interaction;>>Toxoplasmosis;>>Amoebiasis;>>Human papillomavirus infection;>>Pathways in cancer;>>Small cell lung cancer
- 蛋白名称:
- Laminin subunit alpha-3
- 免疫原:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human LAMA3. AA range:2571-2620
- 特异性:
- Laminin α-3 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Laminin α-3 protein.
- 组成:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- 来源:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- 稀释:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:40000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- 纯化工艺:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- 储存:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- 其他名称:
- LAMA3;LAMNA;Laminin subunit alpha-3;Epiligrin 170 kDa subunit;E170;Epiligrin subunit alpha;Kalinin subunit alpha;Laminin-5 subunit alpha;Laminin-6 subunit alpha;Laminin-7 subunit alpha;Nicein subunit alpha
- 背景:
- The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the laminin family of secreted molecules. Laminins are heterotrimeric molecules that consist of alpha, beta, and gamma subunits that assemble through a coiled-coil domain. Laminins are essential for formation and function of the basement membrane and have additional functions in regulating cell migration and mechanical signal transduction. This gene encodes an alpha subunit and is responsive to several epithelial-mesenchymal regulators including keratinocyte growth factor, epidermal growth factor and insulin-like growth factor. Mutations in this gene have been identified as the cause of Herlitz type junctional epidermolysis bullosa and laryngoonychocutaneous syndrome. Alternative splicing and alternative promoter usage result in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2014],
- 功能:
- disease:Defects in LAMA3 are a cause of epidermolysis bullosa junctional Herlitz type (H-JEB) [MIM:226700]; also known as junctional epidermolysis bullosa Herlitz-Pearson type. JEB defines a group of blistering skin diseases characterized by tissue separation which occurs within the dermo-epidermal basement membrane. H-JEB is a severe, infantile and lethal form. Death occurs usually within the first six months of life. Occasionally, children survive to teens. H-JEB is marked by bullous lesions at birth and extensive denudation of skin and mucous membranes that may be hemorrhagic.,disease:Defects in LAMA3 are the cause of laryngoonychocutaneous syndrome (LOCS) [MIM:245660]. LOCS is an autosomal recessive epithelial disorder confined to the Punjabi Muslim population. The condition is characterized by cutaneous erosions, nail dystrophy and exuberant vascular granulation tissue in certain ep
- 细胞定位:
- Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix, basement membrane. Major component.
- 组织表达:
- Skin; respiratory, urinary, and digestive epithelia and in other specialized tissues with prominent secretory or protective functions. Epithelial basement membrane, and epithelial cell tongue that migrates into a wound bed. A differential and focal expression of the subunit alpha-3 is observed in the CNS.
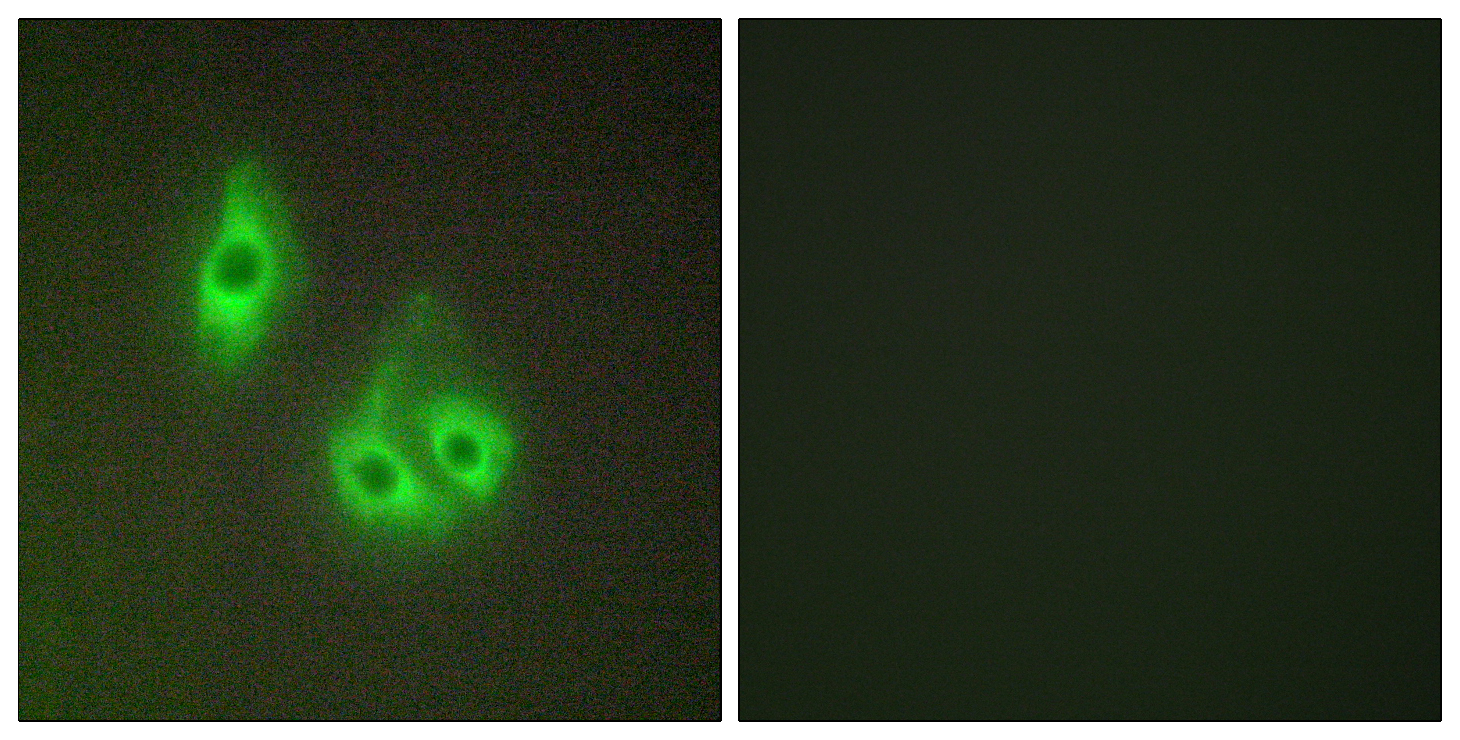
- Immunofluorescence analysis of HepG2 cells, using LAMA3 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
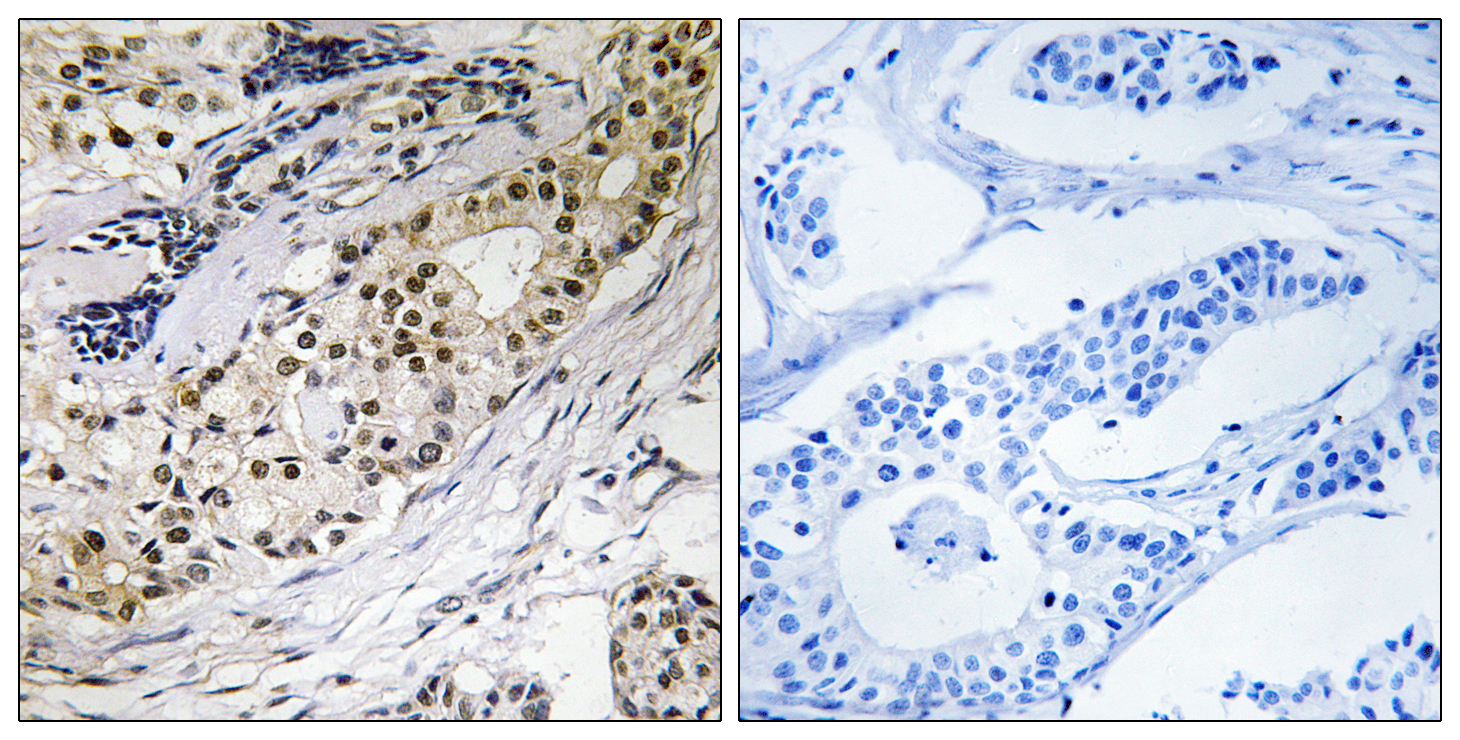
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human colon carcinoma tissue, using LAMA3 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.





