KIR6.2 Polyclonal Antibody
- 货号:YT2479
- 应用:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- 种属:Human;Mouse;Rat
- 简介:
- >>Insulin secretion;>>GnRH secretion;>>Type II diabetes mellitus
- 蛋白名称:
- ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 11
- 免疫原:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Kir6.2. AA range:190-239
- 特异性:
- KIR6.2 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of KIR6.2 protein.
- 组成:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- 来源:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- 稀释:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- 纯化工艺:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- 储存:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- 其他名称:
- KCNJ11;ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 11;IKATP;Inward rectifier K(+) channel Kir6.2;Potassium channel; inwardly rectifying subfamily J member 11
- 背景:
- Potassium channels are present in most mammalian cells, where they participate in a wide range of physiologic responses. The protein encoded by this gene is an integral membrane protein and inward-rectifier type potassium channel. The encoded protein, which has a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into a cell rather than out of a cell, is controlled by G-proteins and is found associated with the sulfonylurea receptor SUR. Mutations in this gene are a cause of familial persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy (PHHI), an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by unregulated insulin secretion. Defects in this gene may also contribute to autosomal dominant non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus type II (NIDDM), transient neonatal diabetes mellitus type 3 (TNDM3), and permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM). Multiple alternatively spliced trans
- 功能:
- disease:Defects in KCNJ11 are a cause of permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM) [MIM:606176]. PNDM is a rare form of diabetes characterized by insulin-requiring hyperglycemia that is diagnosed within the first months of life.,disease:Defects in KCNJ11 are the cause of familial hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia type 2 (HHF2) [MIM:601820]; also known as persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy (PPHI) or hyperinsulinism. HHF2 is the most common cause of persistent hypoglycemia in infancy and is due to defective negative feedback regulation of insulin secretion by low glucose levels. It causes nesidioblastosis, a diffuse abnormality of the pancreas in which there is extensive, often disorganized formation of new islets. Unless early and aggressive intervention is undertaken, brain damage from recurrent episodes of hypoglycemia may occur.,disease:Defects in KCNJ11 are the cause of
- 细胞定位:
- Membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
- 组织表达:
- Brain,Breast,Ovary,Placenta,Spleen,
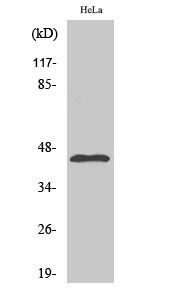
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using KIR6.2 Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:500
.jpg)
- Western Blot analysis of NIH-3T3 cells using KIR6.2 Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:500
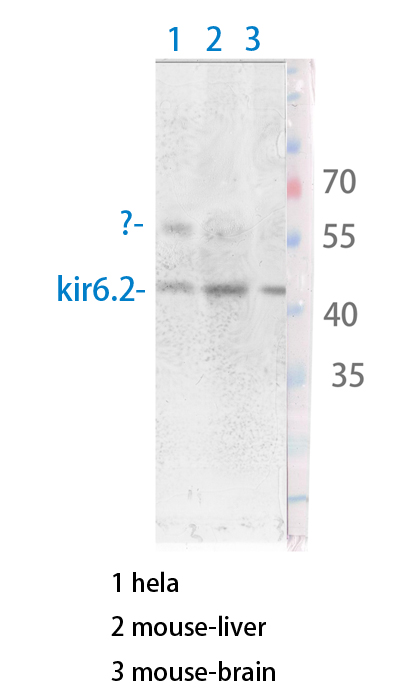
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using Antibody diluted at 1:1000. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS0002) was diluted at 1:20000
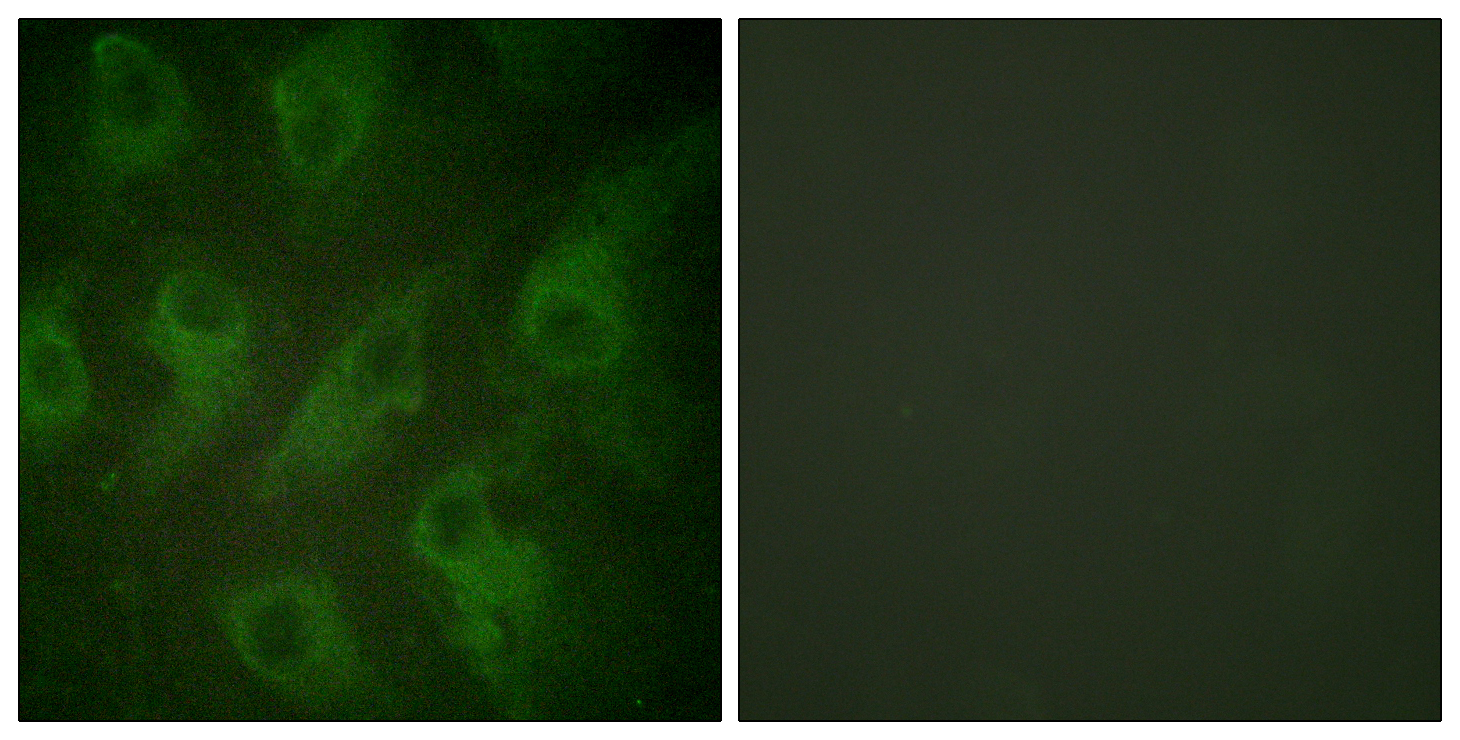
- Immunofluorescence analysis of HeLa cells, using Kir6.2 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
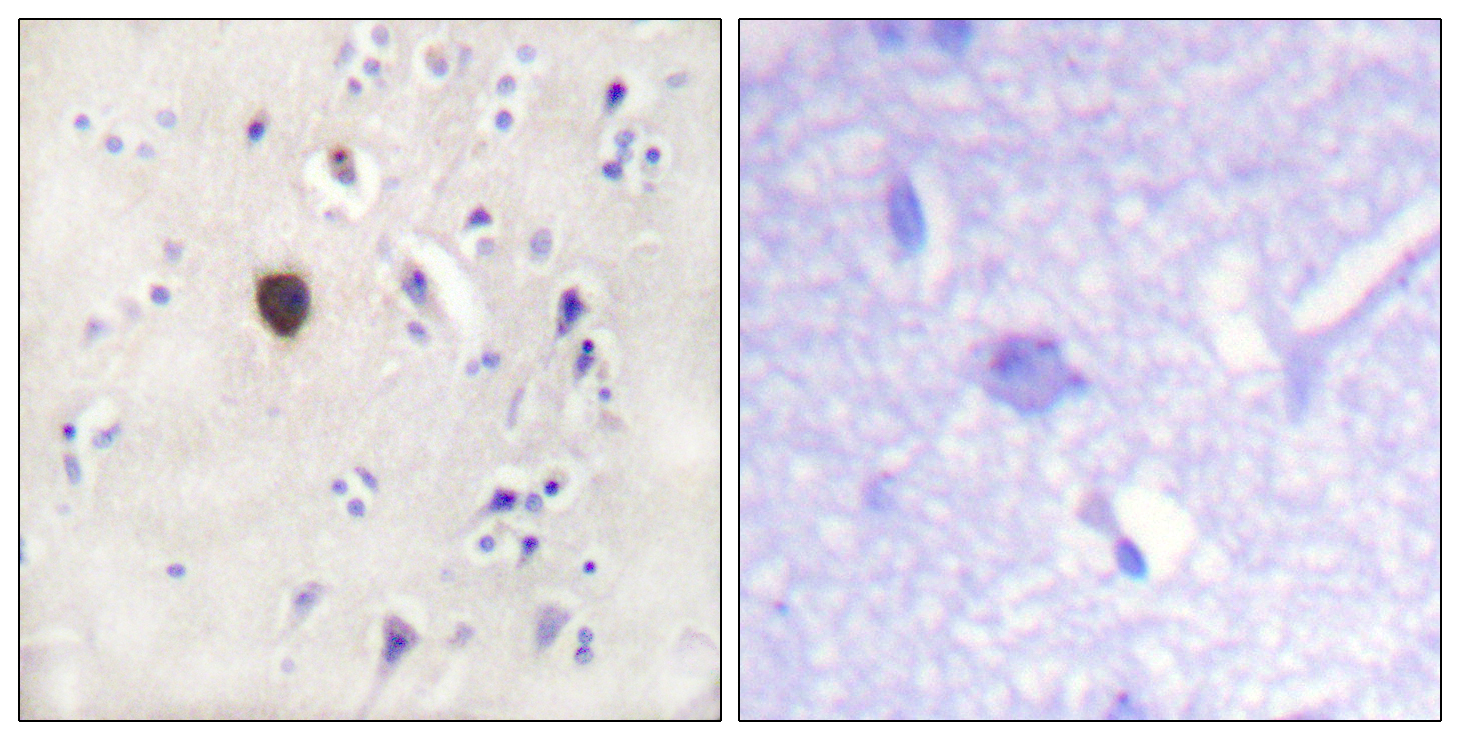
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human brain tissue, using Kir6.2 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.

- Western blot analysis of lysates from 3T3 cells, using Kir6.2 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.

.jpg)







