Ephrin-A2 Polyclonal Antibody
- 货号:YT1590
- 应用:WB;ELISA
- 种属:Human;Mouse
- 简介:
- >>MAPK signaling pathway;>>Ras signaling pathway;>>Rap1 signaling pathway;>>PI3K-Akt signaling pathway;>>Axon guidance;>>MicroRNAs in cancer
- 免疫原:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human EFNA2. AA range:1-50
- 特异性:
- Ephrin-A2 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Ephrin-A2 protein.
- 组成:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- 来源:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- 稀释:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:20000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- 纯化工艺:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- 储存:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- 其他名称:
- EFNA2;EPLG6;LERK6;Ephrin-A2;EPH-related receptor tyrosine kinase ligand 6;LERK-6;HEK7 ligand;HEK7-L
- 背景:
- This gene encodes a member of the ephrin family. The protein is composed of a signal sequence, a receptor-binding region, a spacer region, and a hydrophobic region. The EPH and EPH-related receptors comprise the largest subfamily of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases and have been implicated in mediating developmental events, particularly in the nervous system. Based on their structures and sequence relationships, ephrins are divided into the ephrin-A (EFNA) class, which are anchored to the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol linkage, and the ephrin-B (EFNB) class, which are transmembrane proteins. Posttranslational modifications determine whether this protein localizes to the nucleus or the cytoplasm. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- 功能:
- similarity:Belongs to the ephrin family.,subunit:Binds to the receptor tyrosine kinases EPHA3, EPHA4 and EPHA5.,
- 细胞定位:
- Cell membrane ; Lipid-anchor, GPI-anchor .

- Western Blot analysis of various cells using Ephrin-A2 Polyclonal Antibody
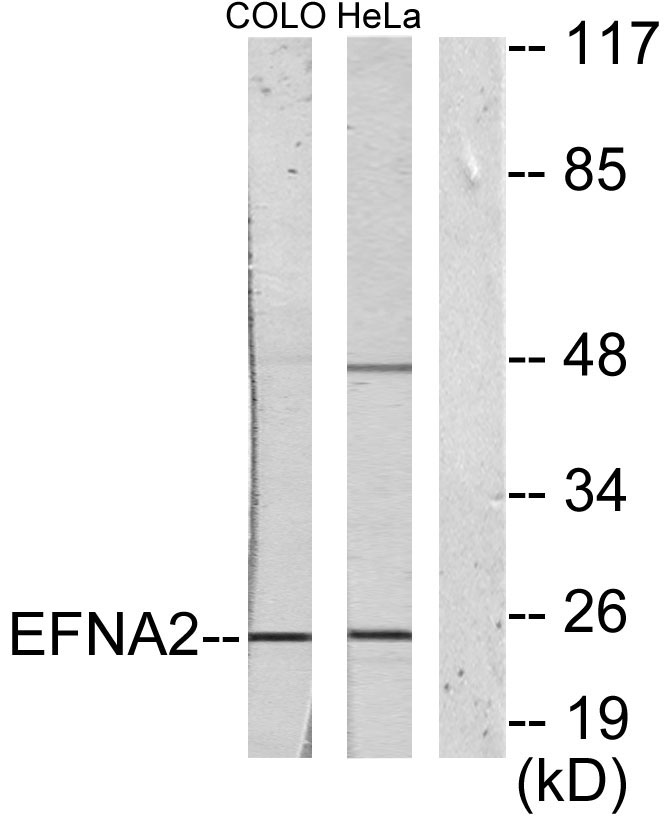
- Western blot analysis of lysates from HeLa and COLO205 cells, using EFNA2 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.





