Cytokeratin 13 Polyclonal Antibody
- 货号:YT1260
- 应用:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- 种属:Human;Mouse;Rat
- 简介:
- >>Estrogen signaling pathway;>>Staphylococcus aureus infection
- 蛋白名称:
- Keratin type I cytoskeletal 13
- 免疫原:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Cytokeratin 13. AA range:233-282
- 特异性:
- Cytokeratin 13 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Cytokeratin 13 protein.
- 组成:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- 来源:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- 稀释:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:5000.. IF 1:50-200
- 纯化工艺:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- 储存:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- 其他名称:
- KRT13;Keratin; type I cytoskeletal 13;Cytokeratin-13;CK-13;Keratin-13;K13
- 背景:
- The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the keratin gene family. The keratins are intermediate filament proteins responsible for the structural integrity of epithelial cells and are subdivided into cytokeratins and hair keratins. Most of the type I cytokeratins consist of acidic proteins which are arranged in pairs of heterotypic keratin chains. This type I cytokeratin is paired with keratin 4 and expressed in the suprabasal layers of non-cornified stratified epithelia. Mutations in this gene and keratin 4 have been associated with the autosomal dominant disorder White Sponge Nevus. The type I cytokeratins are clustered in a region of chromosome 17q21.2. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants; however, not all variants have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- 功能:
- disease:Defects in KRT13 are a cause of white sponge nevus of cannon (WSN) [MIM:193900]. WSN is a rare autosomal dominant disorder which predominantly affects non-cornified stratified squamous epithelia. Clinically, it is characterized by the presence of soft, white, and spongy plaques in the oral mucosa. The characteristic histopathologic features are epithelial thickening, parakeratosis, and vacuolization of the suprabasal layer of oral epithelial keratinocytes. Less frequently the mucous membranes of the nose, esophagus, genitalia and rectum are involved.,miscellaneous:There are two types of cytoskeletal and microfibrillar keratin: I (acidic; 40-55 kDa) and II (neutral to basic; 56-70 kDa).,online information:Keratin-13 entry,PTM:O-glycosylated; glycans consist of single N-acetylglucosamine residues.,similarity:Belongs to the intermediate filament family.,subunit:Heterotetramer of two
- 细胞定位:
- nucleus,intermediate filament,keratin filament,intermediate filament cytoskeleton,extracellular exosome,
- 组织表达:
- Expressed in some epidermal sweat gland ducts (at protein level) and in exocervix, esophagus and placenta.
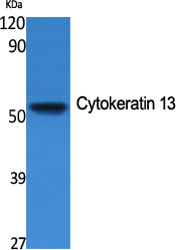
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using Cytokeratin 13 Polyclonal Antibody
.jpg)
- Western Blot analysis of HepG2 cells using Cytokeratin 13 Polyclonal Antibody
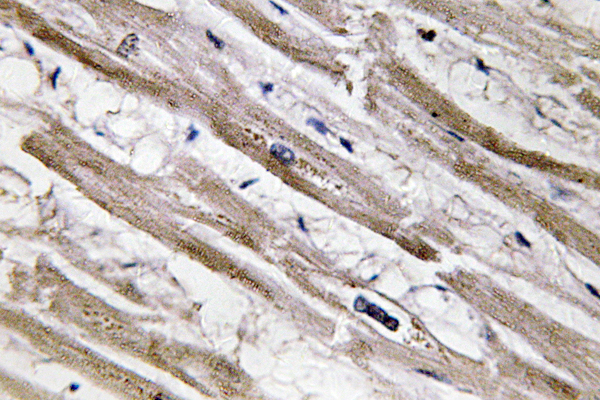
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of Cytokeratin 13 antibody in paraffin-embedded human heart tissue.
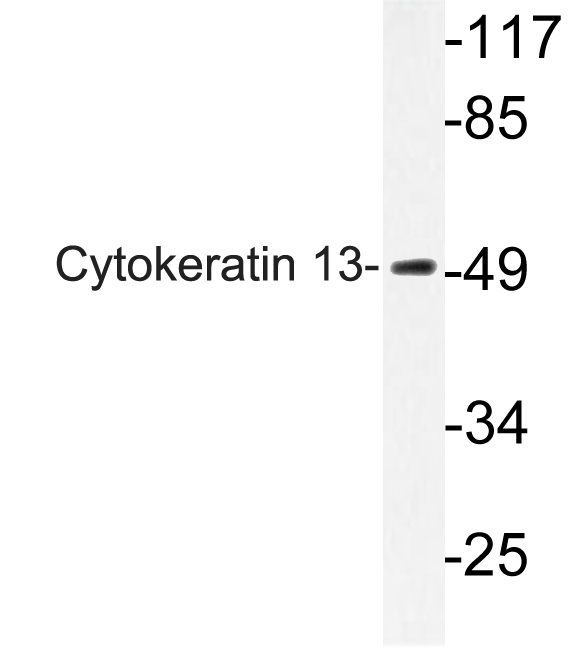
- Western blot analysis of lysate from HepG2 cells, using Cytokeratin 13 antibody.

.jpg)





