Estrogen Receptor α (PTR2124) mouse mAb
- 货号:YM4446
- 应用:IHC;WB;IF;ELISA
- 种属:Human;
- 蛋白名称:
- Estrogen receptor (ER) (ER-alpha) (Estradiol receptor) (Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group A member 1)
- 免疫原:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human Estrogen Receptor α. AA range: 450-595
- 特异性:
- This antibody detects endogenous levels of Estrogen Receptor α protein.
- 组成:
- PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300, 0.05%BSA
- 来源:
- Mouse, Monoclonal/IgG2b, kappa
- 稀释:
- IHC 1:200-1000. WB 1:500-2000. IF 1:100-500. ELISA 1:1000-5000
- 储存:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- 其他名称:
- Estrogen receptor (ER) (ER-alpha) (Estradiol receptor) (Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group A member 1)
- 背景:
- estrogen receptor 1(ESR1) Homo sapiens This gene encodes an estrogen receptor, a ligand-activated transcription factor composed of several domains important for hormone binding, DNA binding, and activation of transcription. The protein localizes to the nucleus where it may form a homodimer or a heterodimer with estrogen receptor 2. Estrogen and its receptors are essential for sexual development and reproductive function, but also play a role in other tissues such as bone. Estrogen receptors are also involved in pathological processes including breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and osteoporosis. Alternative promoter usage and alternative splicing result in dozens of transcript variants, but the full-length nature of many of these variants has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2014],
- 功能:
- Nuclear hormone receptor. The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Ligand-dependent nuclear transactivation involves either direct homodimer binding to a palindromic estrogen response element (ERE) sequence or association with other DNA-binding transcription factors, such as AP-1/c-Jun, c-Fos, ATF-2, Sp1 and Sp3, to mediate ERE-independent signaling. Ligand binding induces a conformational change allowing subsequent or combinatorial association with multiprotein coactivator complexes through LXXLL motifs of their respective components. Mutual transrepression occurs between the estrogen receptor (ER) and NF-kappa-B in a cell-type specific manner. Decreases NF-kappa-B DNA-binding activity and inhibits NF-kappa-B-mediated transcription from the IL6 promoter
- 组织表达:
- Widely expressed (PubMed:10970861). Not expressed in the pituitary gland (PubMed:10970861). ; [Isoform 3]: Widely expressed, however not expressed in the pituitary gland.
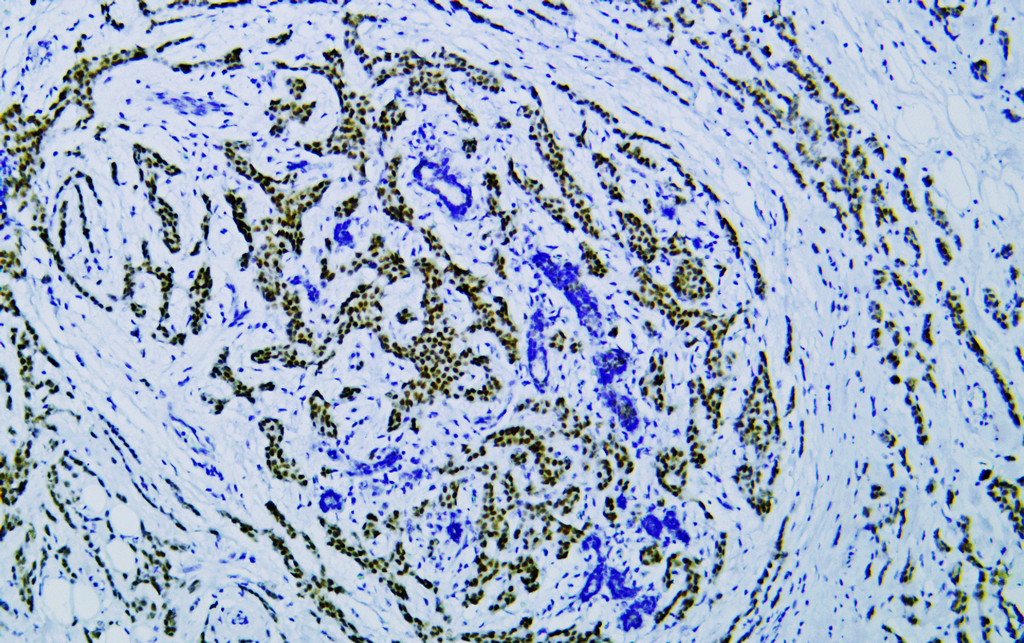
- Human breast carcinoma tissue was stained with Anti-Estrogen Receptor α (PTR2124) Antibody
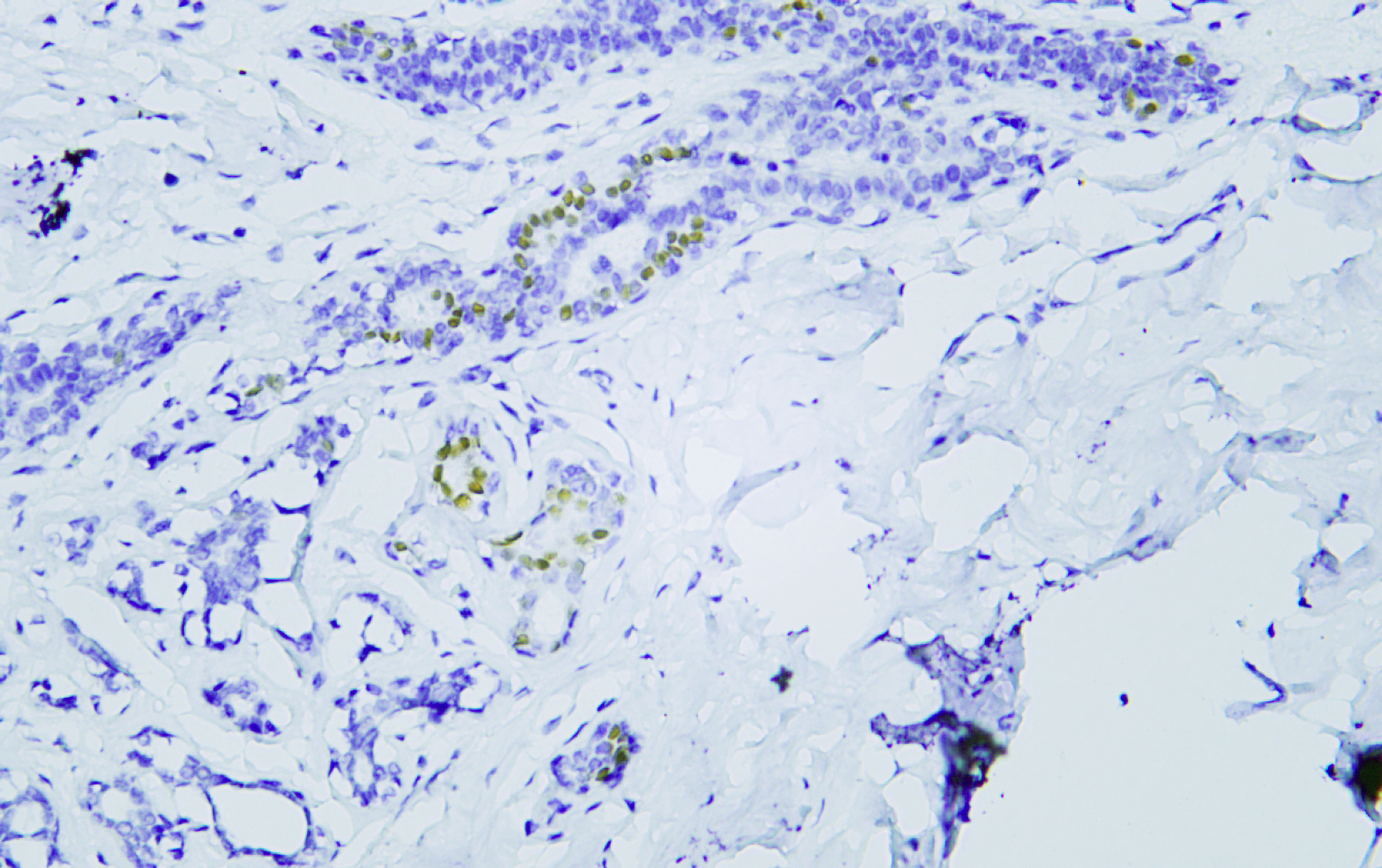
- Human breast tissue was stained with Anti-Estrogen Receptor α (PTR2124) Antibody
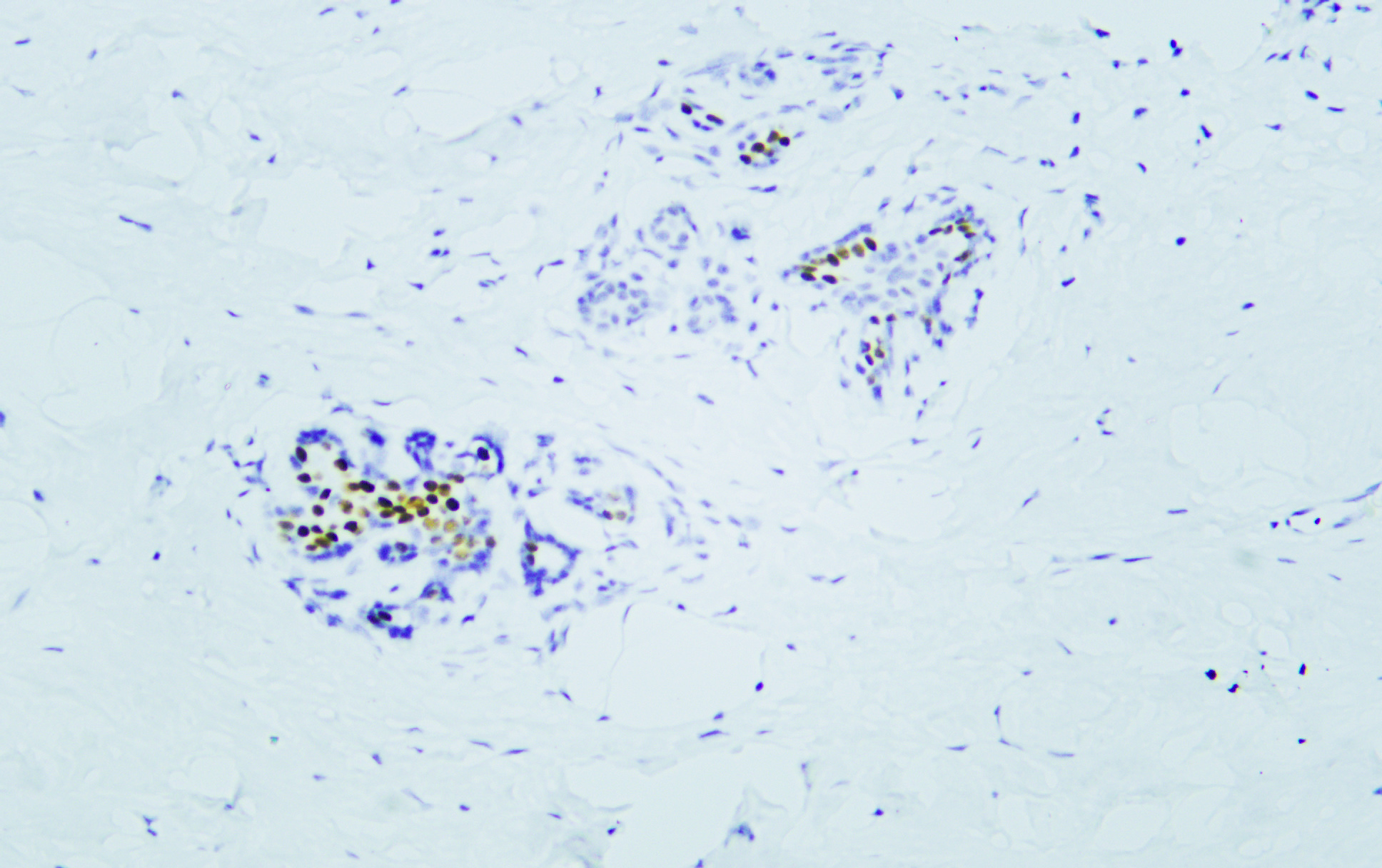
- Human breast tissue was stained with Anti-Estrogen Receptor α (PTR2124) Antibody
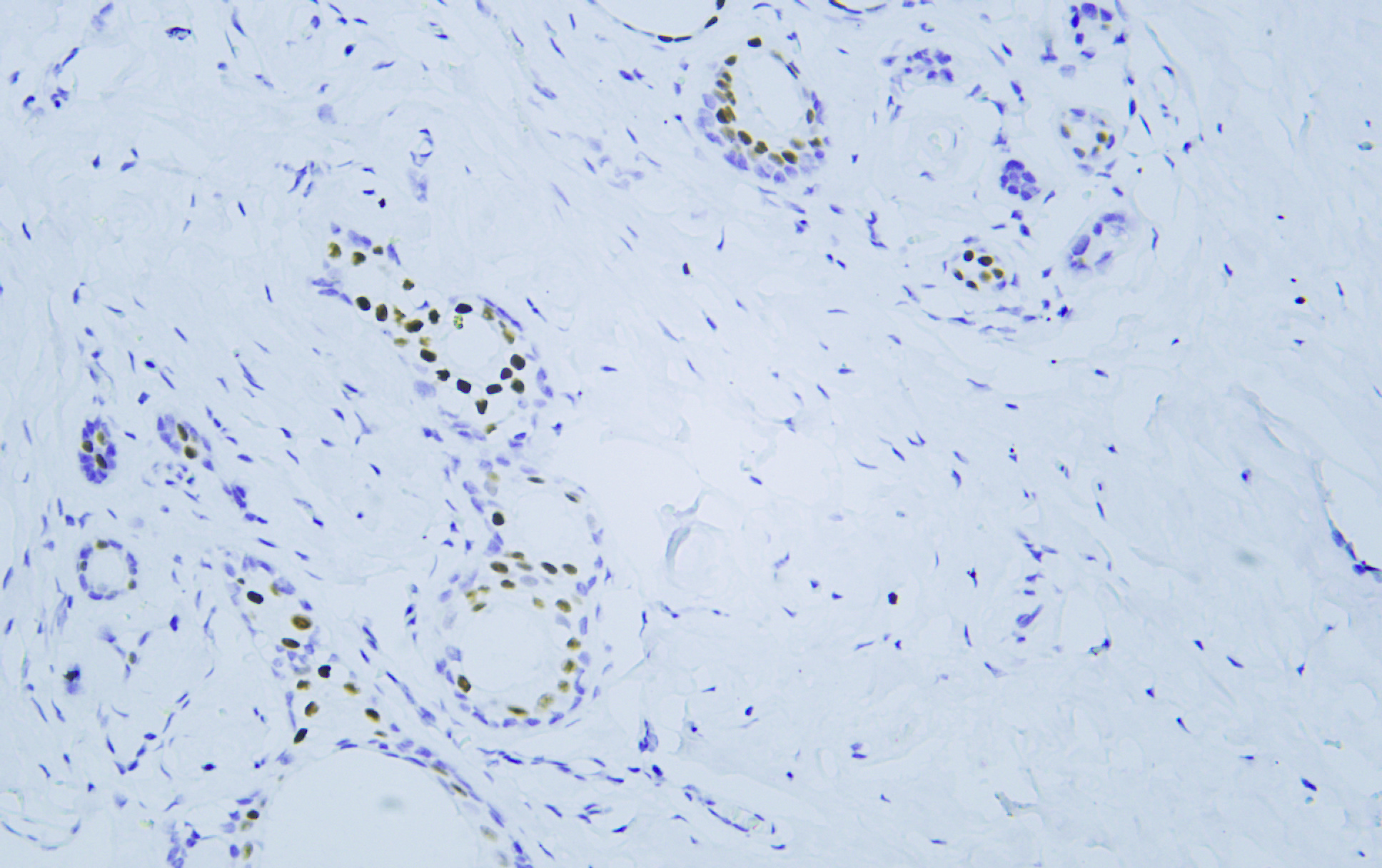
- Human breast tissue was stained with Anti-Estrogen Receptor α (PTR2124) Antibody
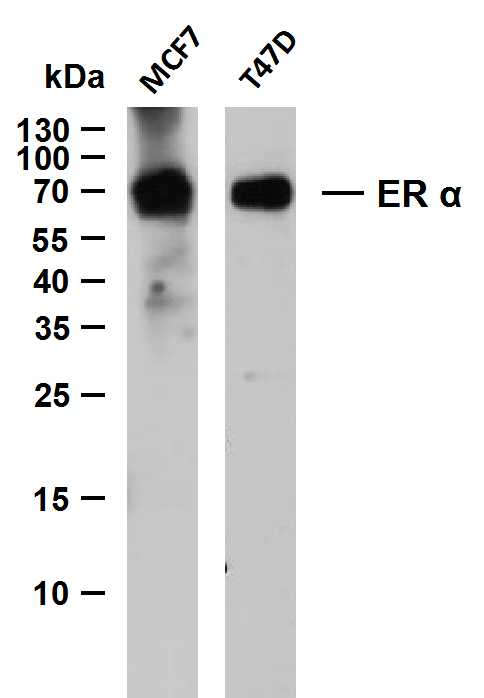
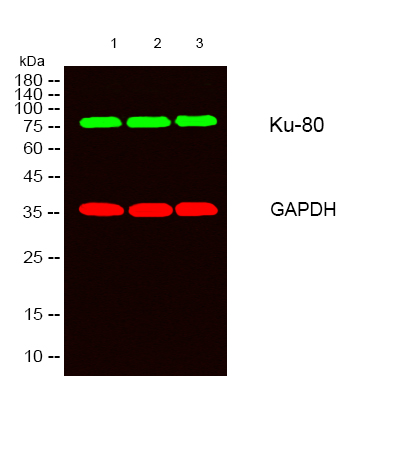
- Various whole cell lysates were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with anti-ER α (PTR2124)antibody. The HRP-conjugated Goat anti-Mouse IgG(H + L) antibody was used to detect the antibody.
Lane 1: MCF7
Lane 2: T47D






