Catalog: YT3750
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
200μL
$450.00
In stock
0
100μL
$280.00
In stock
0
40μL
$150.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Target
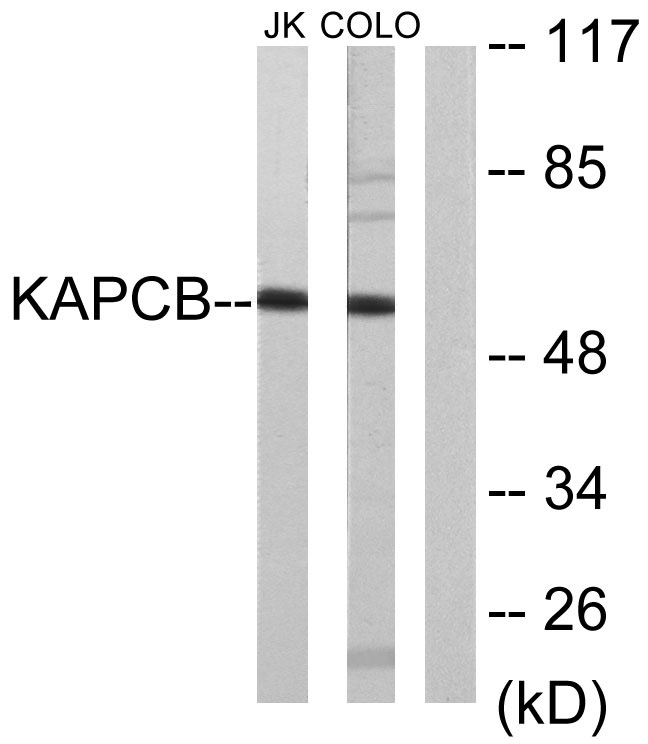
PKAβ cat
Host Species
Rabbit
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
WB, IHC, IF, ELISA
MW
53kD (Observed)
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Recommended Dilution Ratio
WB 1:500-1:2000; IHC 1:100-1:300; ELISA 1:20000; IF 1:50-200
Formulation
Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
Specificity
PKAβ cat Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of PKAβ cat protein.
Purification
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
Storage
-15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
Concentration
1 mg/ml
MW(Observed)
53kD
Modification
Unmodified
Clonality
Polyclonal
Isotype
IgG
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Immunogen:
The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human KAPCB. AA range:291-340
show all
Specificity:
PKAβ cat Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of PKAβ cat protein.
show all
Gene Name:
PRKACB
show all
Protein Name:
cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit beta
show all
Other Name:
PRKACB ;
cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit beta ;
PKA C-beta
cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit beta ;
PKA C-beta
show all
Database Link:
Background:
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the serine/threonine protein kinase family. The encoded protein is a catalytic subunit of cAMP (cyclic AMP)-dependent protein kinase, which mediates signalling though cAMP. cAMP signaling is important to a number of processes, including cell proliferaton and differentiation. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been observed. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014],
show all
Function:
Catalytic activity:ATP + a protein = ADP + a phosphoprotein.,cofactor:Magnesium.,enzyme regulation:Activated by cAMP.,Function:Mediates cAMP-dependent signaling triggered by receptor binding to GPCRs. PKA activation regulates diverse cellular processes such as cell proliferation, the cell cycle, differentiation and regulation of microtubule dynamics, chromatin condensation and decondensation, nuclear envelope disassembly and reassembly, as well as regulation of intracellular transport mechanisms and ion flux.,PTM:Asn-3 is partially deaminated to Asp giving rise to 2 major isoelectric variants, called CB and CA respectively.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. AGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family. cAMP subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 AGC-kinase C-terminal domain.,similarity:Contains 1 protein kinase domain.,subcellular location:Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit) (By similarity). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm.,subunit:A number of inactive tetrameric holoenzymes are produced by the combination of homo- or heterodimers of the different regulatory subunits associated with two catalytic subunits. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits.,tissue specificity:Isoform 1 is most abundant in the brain, with low level expression in kidney. Isoform 2 is predominantly expressed in thymus, spleen and kidney. Isoforms 3 and 4 are only epxressed in the brain.,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Cytoplasm . Cell membrane . Membrane ; Lipid-anchor . Nucleus . Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. .
show all
Tissue Expression:
Isoform 1 is most abundant in the brain, with low level expression in kidney. Isoform 2 is predominantly expressed in thymus, spleen and kidney. Isoform 3 and isoform 4 are only expressed in the brain.
show all
Research Areas:
>>Endocrine resistance ;
>>MAPK signaling pathway ;
>>Ras signaling pathway ;
>>Calcium signaling pathway ;
>>cAMP signaling pathway ;
>>Chemokine signaling pathway ;
>>Oocyte meiosis ;
>>Autophagy - animal ;
>>Longevity regulating pathway ;
>>Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species ;
>>Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes ;
>>Vascular smooth muscle contraction ;
>>Wnt signaling pathway ;
>>Hedgehog signaling pathway ;
>>Apelin signaling pathway ;
>>Tight junction ;
>>Gap junction ;
>>Platelet activation ;
>>Circadian entrainment ;
>>Thermogenesis ;
>>Long-term potentiation ;
>>Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling ;
>>Glutamatergic synapse ;
>>Cholinergic synapse ;
>>Serotonergic synapse ;
>>GABAergic synapse ;
>>Dopaminergic synapse ;
>>Olfactory transduction ;
>>Taste transduction ;
>>Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels ;
>>Insulin signaling pathway ;
>>Insulin secretion ;
>>GnRH signaling pathway ;
>>Ovarian steroidogenesis ;
>>Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation ;
>>Estrogen signaling pathway ;
>>Melanogenesis ;
>>Thyroid hormone synthesis ;
>>Thyroid hormone signaling pathway ;
>>Oxytocin signaling pathway ;
>>Glucagon signaling pathway ;
>>Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes ;
>>Renin secretion ;
>>Aldosterone synthesis and secretion ;
>>Relaxin signaling pathway ;
>>Cortisol synthesis and secretion ;
>>Parathyroid hormone synthesis, secretion and action ;
>>Cushing syndrome ;
>>Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action ;
>>Endocrine and other factor-regulated calcium reabsorption ;
>>Vasopressin-regulated water reabsorption ;
>>Salivary secretion ;
>>Gastric acid secretion ;
>>Bile secretion ;
>>Parkinson disease ;
>>Prion disease ;
>>Cocaine addiction ;
>>Amphetamine addiction ;
>>Morphine addiction ;
>>Alcoholism ;
>>Vibrio cholerae infection ;
>>Amoebiasis ;
>>Human cytomegalovirus infection ;
>>Human papillomavirus infection ;
>>Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection ;
>>Pathways in cancer ;
>>Viral carcinogenesis ;
>>Proteoglycans in cancer ;
>>Chemical carcinogenesis - receptor activation ;
>>Dilated cardiomyopathy
>>MAPK signaling pathway ;
>>Ras signaling pathway ;
>>Calcium signaling pathway ;
>>cAMP signaling pathway ;
>>Chemokine signaling pathway ;
>>Oocyte meiosis ;
>>Autophagy - animal ;
>>Longevity regulating pathway ;
>>Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species ;
>>Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes ;
>>Vascular smooth muscle contraction ;
>>Wnt signaling pathway ;
>>Hedgehog signaling pathway ;
>>Apelin signaling pathway ;
>>Tight junction ;
>>Gap junction ;
>>Platelet activation ;
>>Circadian entrainment ;
>>Thermogenesis ;
>>Long-term potentiation ;
>>Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling ;
>>Glutamatergic synapse ;
>>Cholinergic synapse ;
>>Serotonergic synapse ;
>>GABAergic synapse ;
>>Dopaminergic synapse ;
>>Olfactory transduction ;
>>Taste transduction ;
>>Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels ;
>>Insulin signaling pathway ;
>>Insulin secretion ;
>>GnRH signaling pathway ;
>>Ovarian steroidogenesis ;
>>Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation ;
>>Estrogen signaling pathway ;
>>Melanogenesis ;
>>Thyroid hormone synthesis ;
>>Thyroid hormone signaling pathway ;
>>Oxytocin signaling pathway ;
>>Glucagon signaling pathway ;
>>Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes ;
>>Renin secretion ;
>>Aldosterone synthesis and secretion ;
>>Relaxin signaling pathway ;
>>Cortisol synthesis and secretion ;
>>Parathyroid hormone synthesis, secretion and action ;
>>Cushing syndrome ;
>>Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action ;
>>Endocrine and other factor-regulated calcium reabsorption ;
>>Vasopressin-regulated water reabsorption ;
>>Salivary secretion ;
>>Gastric acid secretion ;
>>Bile secretion ;
>>Parkinson disease ;
>>Prion disease ;
>>Cocaine addiction ;
>>Amphetamine addiction ;
>>Morphine addiction ;
>>Alcoholism ;
>>Vibrio cholerae infection ;
>>Amoebiasis ;
>>Human cytomegalovirus infection ;
>>Human papillomavirus infection ;
>>Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection ;
>>Pathways in cancer ;
>>Viral carcinogenesis ;
>>Proteoglycans in cancer ;
>>Chemical carcinogenesis - receptor activation ;
>>Dilated cardiomyopathy
show all
Signaling Pathway
Cellular Processes >> Transport and catabolism >> Autophagy - animal
Cellular Processes >> Cellular community - eukaryotes >> Tight junction
Cellular Processes >> Cellular community - eukaryotes >> Gap junction
Organismal Systems >> Immune system >> Platelet activation
Organismal Systems >> Immune system >> Chemokine signaling pathway
Organismal Systems >> Endocrine system >> Insulin secretion
Organismal Systems >> Endocrine system >> Insulin signaling pathway
Organismal Systems >> Endocrine system >> Glucagon signaling pathway
Organismal Systems >> Endocrine system >> GnRH signaling pathway
Organismal Systems >> Endocrine system >> Estrogen signaling pathway
Organismal Systems >> Endocrine system >> Oxytocin signaling pathway
Organismal Systems >> Endocrine system >> Relaxin signaling pathway
Organismal Systems >> Endocrine system >> Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action
Organismal Systems >> Endocrine system >> Thyroid hormone signaling pathway
Organismal Systems >> Endocrine system >> Aldosterone synthesis and secretion
Organismal Systems >> Circulatory system >> Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes
Organismal Systems >> Circulatory system >> Vascular smooth muscle contraction
Organismal Systems >> Nervous system >> Glutamatergic synapse
Organismal Systems >> Nervous system >> Cholinergic synapse
Organismal Systems >> Nervous system >> Dopaminergic synapse
Organismal Systems >> Sensory system >> Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels
Organismal Systems >> Aging >> Longevity regulating pathway
Organismal Systems >> Aging >> Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> Pathways in cancer
Human Diseases >> Neurodegenerative disease >> Parkinson disease
Human Diseases >> Neurodegenerative disease >> Prion disease
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> MAPK signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Ras signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Wnt signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Hedgehog signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Apelin signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Calcium signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> cAMP signaling pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: YT3750
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
200μL
$450.00
In stock
0
100μL
$280.00
In stock
0
40μL
$150.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}