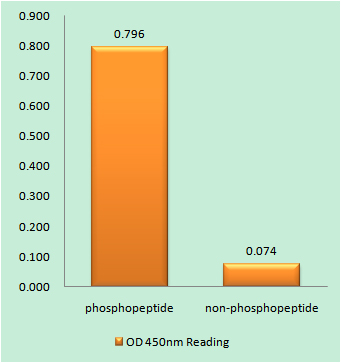
Catalog: KA4264C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Reactivity
Human, Mouse
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months
Modification
Unmodified
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
RELB
show all
Other Name:
Transcription factor RelB ;
I-Rel ;
I-Rel ;
show all
Background:
caution:Was originally (PubMed:1577270) thought to inhibit the transcriptional activity of nuclear factor NF-kappa-B.,domain:Both N- and C-terminal domains are required for transcriptional activation.,function:NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor which is present in almost all cell types and is involved in many biological processed such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus. NF-kappa-B heterodimeric RelB-p50 and RelB-p52 complexes are transcriptional activators. RELB neither associates with DNA nor with RELA/p65 or REL. Stimulates promoter activity in the presence of NFKB2/p49.,induction:By mitogens.,PTM:Phosphorylation at 'Thr-103' and 'Ser-573' is followed by proteasomal degradation.,similarity:Contains 1 RHD (Rel-like) domain.,subunit:Component of the NF-kappa-B RelB-p50 complex. Component of the NF-kappa-B RelB-p52 complex. Self-associates; the interaction seems to be transient and may prevent degradation allowing for heterodimer formation with p50 or p52. Interacts with NFKB1/p50, NFKB2/p52 and NFKB2/p100. Interacts with NFKBID.,
show all
Function:
myeloid dendritic cell activation, cell activation, adaptive immune response, cell activation during immune response,myeloid leukocyte activation, lymphocyte activation during immune response, T cell activation during immune response, alpha-beta T cell activation during immune response, T cell differentiation during immune response, alpha-beta T cell differentiation during immune response, CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation during immune response, leukocyte activation during immune response, adaptive immune response based on somatic recombination of immune receptors built from immunoglobulin superfamily domains, immune system development, leukocyte differentiation, myeloid leukocyte differentiation, transcription, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, immune response, antigen processing and presentation, hemopoiesis, lymphocyte differentiation, myeloid cell differentiation, T cell differentiation, T-helper 1 type immune response, T-helper cell differentiation, T cell activation, myeloid dendritic cell differentiation, CD4-positive, alpha beta T cell differentiation, T-helper 1 cell differentiation, leukocyte activation,regulation of transcription, alpha-beta T cell activation, alpha-beta T cell differentiation, lymphocyte activation,hemopoietic or lymphoid organ development, regulation of RNA metabolic process,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Nucleus . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome . Colocalizes with NEK6 in the centrosome.
show all
Signaling Pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA4264C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}