Catalog: YM6548
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
200μL
$600.00
In stock
0
100μL
$340.00
In stock
0
40μL
$190.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Target
TSHB
Host Species
Mouse
Reactivity
Human
Applications
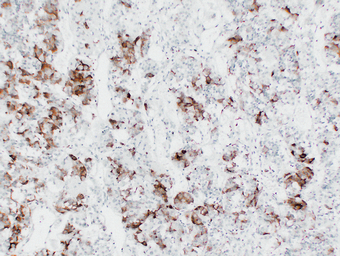
IHC, IF, ELISA
MW
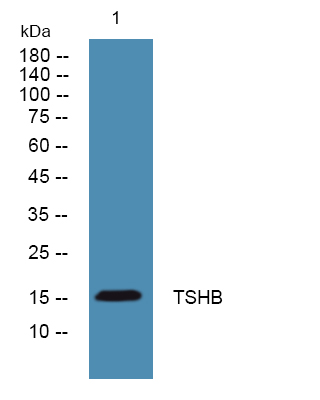
16kD (Calculated)
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Recommended Dilution Ratio
IHC 1:200-400; IF 1:50-200; ELISA 1:500-5000
Formulation
PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300, 0.05%BSA
Specificity
The antibody can specifically recognize human TSH protein.
Purification
The antibody was affinity-purified from ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
Storage
-15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
MW(Calculated)
16kD
Modification
Unmodified
Clonality
Monoclonal
Clone Number
ABT-TSH
Isotype
IgG1,Lambda
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Immunogen:
Synthesized peptide derived from human Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone(TSH) AA range: 50-138
show all
Specificity:
The antibody can specifically recognize human TSH protein.
show all
Gene Name:
TSHB
show all
Protein Name:
Thyrotropin subunit beta (Thyroid-stimulating hormone subunit beta) (TSH-B) (TSH-beta) (Thyrotropin beta chain) (Thyrotropin alfa)
show all
Background:
The four human glycoprotein hormones chorionic gonadotropin (CG), luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) are dimers consisting of alpha and beta subunits that are associated noncovalently. The alpha subunits of these hormones are identical, however, their beta chains are unique and confer biological specificity. Thyroid stimulating hormone functions in the control of thyroid structure and metabolism. The protein encoded by this gene is the beta subunit of thyroid stimulating hormone. Mutations in this gene are associated with congenital central and secondary hypothyroidism and Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013],
show all
Function:
Function:Indispensable for the control of thyroid structure and metabolism.,online information:Clinical information on Thyrogen,online information:Thyroid-stimulating hormone entry,pharmaceutical:Available under the name Thyrogen (Genzyme). Used in combination with other tests to detect recurring or leftover thyroid cancer cells in patients with a history of certain types of thyroid cancer.,similarity:Belongs to the glycoprotein hormones subunit beta family.,subunit:Heterodimer of a common alpha chain and a unique beta chain which confers biological specificity to thyrotropin, lutropin, follitropin and gonadotropin.,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Cytoplasmic
show all
Research Areas:
>>cAMP signaling pathway ;
>>Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction ;
>>Thyroid hormone synthesis ;
>>Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes ;
>>Autoimmune thyroid disease
>>Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction ;
>>Thyroid hormone synthesis ;
>>Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes ;
>>Autoimmune thyroid disease
show all
Signaling Pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: YM6548
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
200μL
$600.00
In stock
0
100μL
$340.00
In stock
0
40μL
$190.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}