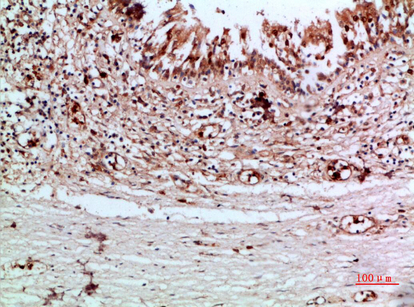
Catalog: IHCM6224
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
100mL
$2,960.00
3 weeks
0
10mL
$356.00
3 weeks
0
3mL
$156.00
3 weeks
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Target
Thyroglobulin
Host Species
Mouse
Reactivity
Human
Applications
IHC
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Specificity
The antibody can specifically recognize human Thyroglobulin protein.
Purification
The antibody was affinity-purified from ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
Storage
2°C to 8°C/1 year,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Unmodified
Clonality
Monoclonal
Clone Number
PT0653
Isotype
IgG1,Kappa
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Immunogen:
Synthesized peptide derived from human Thyroglobulin AA range: 2700-2768
show all
Specificity:
The antibody can specifically recognize human Thyroglobulin protein.
show all
Gene Name:
TG
show all
Protein Name:
Thyroglobulin
show all
Other Name:
Thyroglobulin ;
Tg ;
Tg ;
show all
Background:
Thyroglobulin (Tg) is a glycoprotein homodimer produced predominantly by the thryroid gland. It acts as a substrate for the synthesis of thyroxine and triiodothyronine as well as the storage of the inactive forms of thyroid hormone and iodine. Thyroglobulin is secreted from the endoplasmic reticulum to its site of iodination, and subsequent thyroxine biosynthesis, in the follicular lumen. Mutations in this gene cause thyroid dyshormonogenesis, manifested as goiter, and are associated with moderate to severe congenital hypothyroidism. Polymorphisms in this gene are associated with susceptibility to autoimmune thyroid diseases (AITD) such as Graves disease and Hashimoto thryoiditis. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009],
show all
Function:
Disease:Defects in TG are a cause of some forms of goiter [MIM:188450]. Goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid gland. This is sometimes linked to hypothyroidism.,Disease:Variations in TG are associated with susceptibility to autoimmune thyroid disease type 3 (AITD3) [MIM:608175]. AITDs including Graves disease (GD) and Hashimoto thyroiditis (HT), are among the most common human autoimmune diseases. They are complex diseases, which are caused by an interaction between susceptibility genes and nongenetic factors, such as infection.,Function:Precursor of the iodinated thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).,online information:Thyroglobulin entry,PTM:Sulfated.,similarity:Belongs to the type-B carboxylesterase/lipase family.,similarity:Contains 11 thyroglobulin type-1 domains.,subunit:Homodimer.,tissue specificity:Thyroid gland specific.,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Cytoplasmic
show all
Tissue Expression:
Research Areas:
>>Thyroid hormone synthesis ;
>>Autoimmune thyroid disease
>>Autoimmune thyroid disease
show all
Signaling Pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: IHCM6224
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
100mL
$2,960.00
3 weeks
0
10mL
$356.00
3 weeks
0
3mL
$156.00
3 weeks
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}