Catalog: IHCM6214
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
100mL
$2,960.00
3 weeks
0
10mL
$356.00
3 weeks
0
3mL
$156.00
3 weeks
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Target
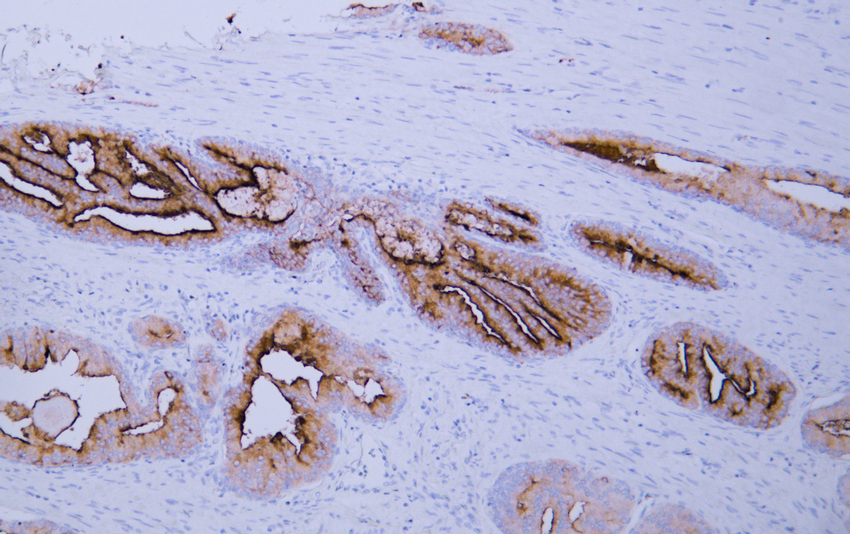
Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA)
Host Species
Mouse
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
IHC
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Specificity
The antibody can specifically recognize human PSMA protein.
Purification
The antibody was affinity-purified from ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
Storage
2°C to 8°C/1 year,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Unmodified
Clonality
Monoclonal
Clone Number
ABT-PSMA
Isotype
IgG1,Kappa
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Immunogen:
Synthesized peptide derived from human Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA) AA range: 100-200
show all
Specificity:
The antibody can specifically recognize human PSMA protein.
show all
Gene Name:
FOLH1 FOLH NAALAD1 PSM PSMA GIG27
show all
Protein Name:
Glutamate carboxypeptidase 2 (Cell growth-inhibiting gene 27 protein) (Folate hydrolase 1) (Folylpoly-gamma-glutamate carboxypeptidase) (FGCP) (Glutamate carboxypeptidase II) (GCPII) (Membrane glutamate carboxypeptidase) (mGCP) (N-acetylated-alpha-linked acidic dipeptidase I) (NAALADase I) (Prostate-specific membrane antigen) (PSM) (PSMA) (Pteroylpoly-gamma-glutamate carboxypeptidase)
show all
Background:
This gene encodes a type II transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the M28 peptidase family. The protein acts as a glutamate carboxypeptidase on different alternative substrates, including the nutrient folate and the neuropeptide N-acetyl-l-aspartyl-l-glutamate and is expressed in a number of tissues such as prostate, central and peripheral nervous system and kidney. A mutation in this gene may be associated with impaired intestinal absorption of dietary folates, resulting in low blood folate levels and consequent hyperhomocysteinemia. Expression of this protein in the brain may be involved in a number of pathological conditions associated with glutamate excitotoxicity. In the prostate the protein is up-regulated in cancerous cells and is used as an effective diagnostic and prognostic indicator of prostate cancer. This gene likely arose from a duplication event of a nearby chromosomal region. Alter
show all
Function:
Alternative products:Experimental confirmation may be lacking for some isoforms,Catalytic activity:Release of an unsubstituted, C-terminal glutamyl residue, typically from Ac-Asp-Glu or folylpoly-gamma-glutamates.,cofactor:Binds 2 zinc ions per subunit. Required for NAALADase activity.,Domain:The NAALADase activity is found in the central region, the dipeptidyl peptidase IV type activity in the C-terminal.,enzyme regulation:The NAALADase activity is inhibited by beta-NAAG, quisqualic acid, 2-(phosphonomethyl) pentanedioic acid (PMPA) and EDTA. Activated by cobalt.,Function:Also exhibits a dipeptidyl-peptidase IV type activity. In vitro, cleaves Gly-Pro-AMC.,Function:Has both folate hydrolase and N-acetylated-alpha-linked-acidic dipeptidase (NAALADase) activity. Has a preference for tri-alpha-glutamate peptides. In the intestine, required for the uptake of folate. In the brain, modulates excitatory neurotransmission through the hydrolysis of the neuropeptide, N-aceylaspartylglutamate (NAAG), thereby releasing glutamate. Isoforms PSM-4 and PSM-5 would appear to be physiologically irrelevant. Involved in prostate tumor progression.,induction:In the prostate, up-regulated in response to androgen deprivation.,miscellaneous:PSMA is used as a diagnostic and prognostic indicator of prostate cancer, and as a possible marker for various neurological disorders such as schizophrenia, Alzheimer disease and Huntington disease.,polymorphism:Genetic variation in FOLH1 may be associated with low folate levels and consequent hyperhomocysteinemia. This condition can result in increased risk of cardiovascular disease, neural tube defects, and cognitive deficits.,PTM:The first two amino acids at the N-terminus of isoform PSMA' appear to be cleaved by limited proteolysis.,PTM:The N-terminus is blocked.,similarity:Belongs to the peptidase M28 family. M28B subfamily.,tissue specificity:Highly expressed in prostate epithelium. Also expressed, in the small intestine, brain, kidney, liver, spleen, colon, trachea, spinal cord and the capillary endothelium of a variety of tumors. Expressed specifically in jejunum brush border membranes. In the brain, highly expressed in the ventral striatum and brain stem. Also expressed in fetal liver and kidney. In the prostate, the PSMA' cytosolic isoform is the most abundant form in normal tissue, the membrane-bound PSMA-1 form in primary prostate tumors. The PSMA-2 isoform also found in normal prostate as well as in brain and liver.,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Cytoplasmic, Membranous
show all
Research Areas:
>>Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism ;
>>Metabolic pathways ;
>>Vitamin digestion and absorption
>>Metabolic pathways ;
>>Vitamin digestion and absorption
show all
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: IHCM6214
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
100mL
$2,960.00
3 weeks
0
10mL
$356.00
3 weeks
0
3mL
$156.00
3 weeks
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}