Lunatic Fringe Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT2605
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- Lunatic Fringe
- Fields:
- >>Other types of O-glycan biosynthesis;>>Notch signaling pathway;>>Human papillomavirus infection
- Gene Name:
- LFNG
- Protein Name:
- Beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase lunatic fringe
- Human Gene Id:
- 3955
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q8NES3
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 16848
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- O09010
- Rat Gene Id:
- 170905
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q924T4
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human LFNG. AA range:121-170
- Specificity:
- Lunatic Fringe Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Lunatic Fringe protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- LFNG;Beta-1;3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase lunatic fringe;O-fucosylpeptide 3-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase
- Observed Band(KD):
- 42kD
- Background:
- This gene is a member of the fringe gene family which also includes radical and manic fringe genes. They all encode evolutionarily conserved glycosyltransferases that act in the Notch signaling pathway to define boundaries during embryonic development. While their genomic structure is distinct from other glycosyltransferases, fringe proteins have a fucose-specific beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity that leads to elongation of O-linked fucose residues on Notch, which alters Notch signaling. This gene product is predicted to be a single-pass type II Golgi membrane protein but it may also be secreted and proteolytically processed like the related proteins in mouse and Drosophila (PMID: 9187150). Mutations in this gene have been associated with autosomal recessive spondylocostal dysostosis 3. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms
- Function:
- alternative products:Experimental confirmation may be lacking for some isoforms,catalytic activity:Transfers a beta-D-GlcNAc residue from UDP-D-GlcNAc to the fucose residue of a fucosylated protein acceptor.,caution:The sequence shown here is derived from an Ensembl automatic analysis pipeline and should be considered as preliminary data.,disease:Defects in LFNG are the cause of spondylocostal dysostosis autosomal recessive type 3 (SCDO3) [MIM:609813]. Autosomal recessive spondylocostal dysostosis is a rare condition of variable severity associated with vertebral and rib segmentation defects. The main skeletal malformations include fusion of vertebrae, hemivertebrae, fusion of certain ribs, and other rib malformations. Deformity of the chest and spine (severe scoliosis, kyphoscoliosis and lordosis) is a natural consequence of the malformation and leads to a dwarf-like appearance. As the
- Subcellular Location:
- Golgi apparatus membrane ; Single-pass type II membrane protein .
- Expression:
- Kidney,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
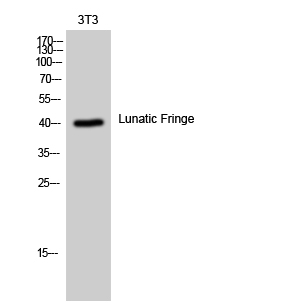
- Western Blot analysis of 3T3 cells using Lunatic Fringe Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:1000
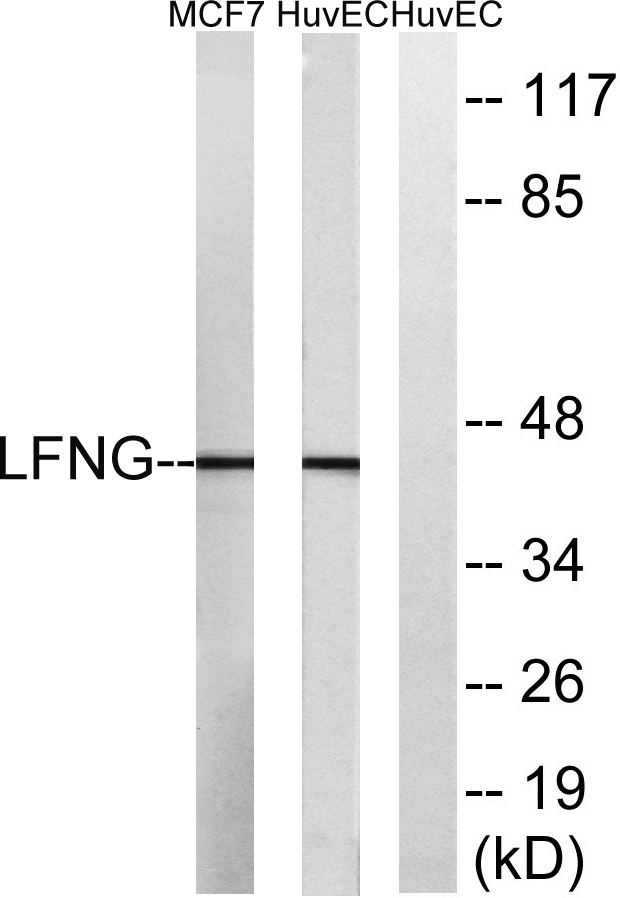
- Western blot analysis of lysates from HUVEC and MCF-7 cells, using LFNG Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.



