EAAT3 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT1449
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- EAAT3
- Fields:
- >>Synaptic vesicle cycle;>>Glutamatergic synapse;>>Protein digestion and absorption
- Gene Name:
- SLC1A1
- Protein Name:
- Excitatory amino acid transporter 3
- Human Gene Id:
- 6505
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P43005
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 20510
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P51906
- Rat Gene Id:
- 25550
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P51907
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human EAAT3. AA range:122-171
- Specificity:
- EAAT3 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of EAAT3 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- SLC1A1;EAAC1;EAAT3;Excitatory amino acid transporter 3;Excitatory amino-acid carrier 1;Neuronal and epithelial glutamate transporter;Sodium-dependent glutamate/aspartate transporter 3;Solute carrier family 1 member 1
- Observed Band(KD):
- 57kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a member of the high-affinity glutamate transporters that play an essential role in transporting glutamate across plasma membranes. In brain, these transporters are crucial in terminating the postsynaptic action of the neurotransmitter glutamate, and in maintaining extracellular glutamate concentrations below neurotoxic levels. This transporter also transports aspartate, and mutations in this gene are thought to cause dicarboxylicamino aciduria, also known as glutamate-aspartate transport defect. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in SLC1A1 may be a cause of dicarboxylicamino aciduria [MIM:222730]; also known as glutamate-aspartate transport defect. This is as defect in renal and probably intestinal transport of glutamic and aspartic acids and is associated with moderate hyperprolinemia.,function:Transports L-glutamate and also L- and D-aspartate. Essential for terminating the postsynaptic action of glutamate by rapidly removing released glutamate from the synaptic cleft. Acts as a symport by cotransporting sodium. Negatively regulated by ARL6IP5.,PTM:Glycosylated.,similarity:Belongs to the sodium:dicarboxylate (SDF) symporter (TC 2.A.23) family.,subunit:Interacts with ARL6IP5/PRAF3.,tissue specificity:Expressed in all tissues tested including liver, muscle, testis, ovary, retinoblastoma cell line, neurons and brain (in which there was dense expression in substantia nigra, red nucleus, hippocampus
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Apical cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Cell junction, synapse, synaptosome . Early endosome membrane . Late endosome membrane . Recycling endosome membrane .
- Expression:
- Expressed in all tissues tested including liver, muscle, testis, ovary, retinoblastoma cell line, neurons and brain (in which there was dense expression in substantia nigra, red nucleus, hippocampus and in cerebral cortical layers).
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
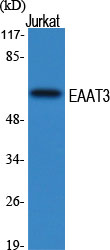
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using EAAT3 Polyclonal Antibody
.jpg)
- Western Blot analysis of 293 cells using EAAT3 Polyclonal Antibody
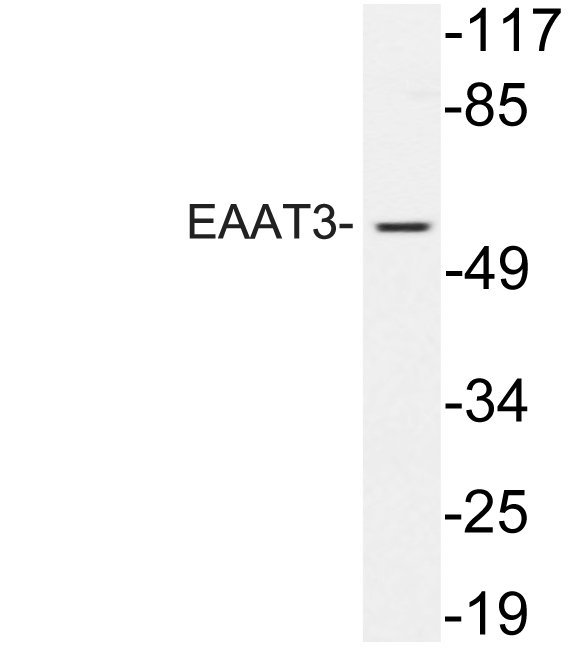
- Western blot analysis of lysate from 293 cells treated with EGF, using EAAT3 antibody.



