SOD1 (PT0113R) PT® Rabbit mAb
- Catalog No.:YM8065
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;IP;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human; Mouse; Rat;
- Target:
- SOD-1
- Fields:
- >>Peroxisome;>>Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species;>>Parkinson disease;>>Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis;>>Huntington disease;>>Prion disease;>>Pathways of neurodegeneration - multiple diseases;>>Chemical carcinogenesis - reactive oxygen species
- Gene Name:
- SOD1
- Protein Name:
- Superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn]
- Human Gene Id:
- 6647
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P00441
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 20655
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P08228
- Rat Gene Id:
- 24786
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P07632
- Specificity:
- endogenous
- Formulation:
- PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300, 0.05%BSA
- Source:
- Monoclonal, rabbit, IgG, Kappa
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:100-1:5000;WB 1:2000-1:10000;IF 1:200-1:1000;ELISA 1:5000-1:20000;IP 1:50-1:200;
- Purification:
- Protein A
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- SOD1;Superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn];Superoxide dismutase 1;hSod1
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 23kD
- Observed Band(KD):
- 15kD
- Background:
- The protein encoded by this gene binds copper and zinc ions and is one of two isozymes responsible for destroying free superoxide radicals in the body. The encoded isozyme is a soluble cytoplasmic protein, acting as a homodimer to convert naturally-occuring but harmful superoxide radicals to molecular oxygen and hydrogen peroxide. The other isozyme is a mitochondrial protein. Mutations in this gene have been implicated as causes of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Rare transcript variants have been reported for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:2 superoxide + 2 H(+) = O(2) + H(2)O(2).,cofactor:Binds 1 copper ion per subunit.,cofactor:Binds 1 zinc ion per subunit.,disease:Defects in SOD1 are the cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis type 1 (ALS1) [MIM:105400]. ALS1 is a familial form of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, a neurodegenerative disorder affecting upper and lower motor neurons and resulting in fatal paralysis. Sensory abnormalities are absent. Death usually occurs within 2 to 5 years. The etiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is likely to be multifactorial, involving both genetic and environmental factors. The disease is inherited in 5-10% of cases leading to familial forms.,function:Destroys radicals which are normally produced within the cells and which are toxic to biological systems.,miscellaneous:The protein (both wild-type and ALS1 variants) has a tendency to form fibrillar aggregates in the
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm, Nucleus
- Expression:
- Colon,Fetal brain cortex,Placenta,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
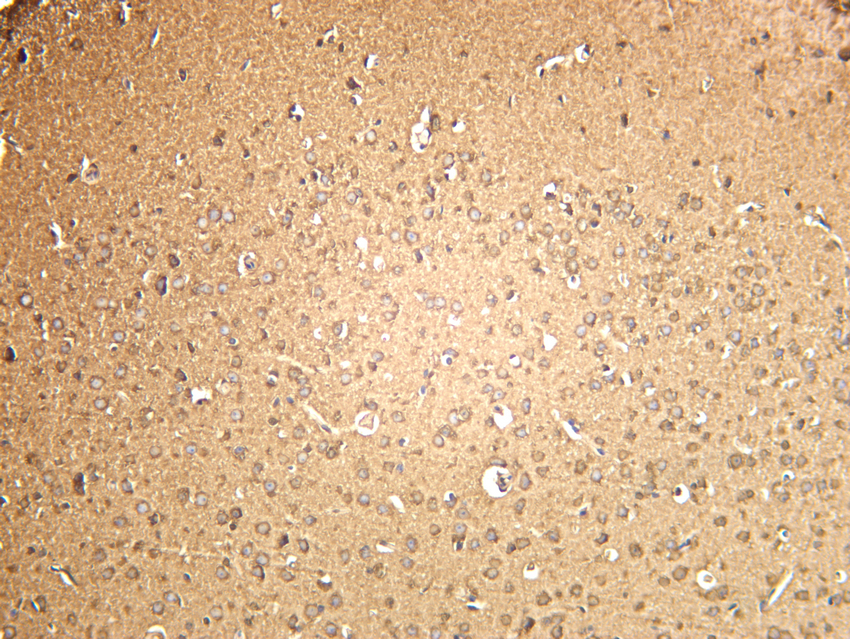
- Mouse brain was stained with anti-SOD1 (PT0113R) rabbit antibody
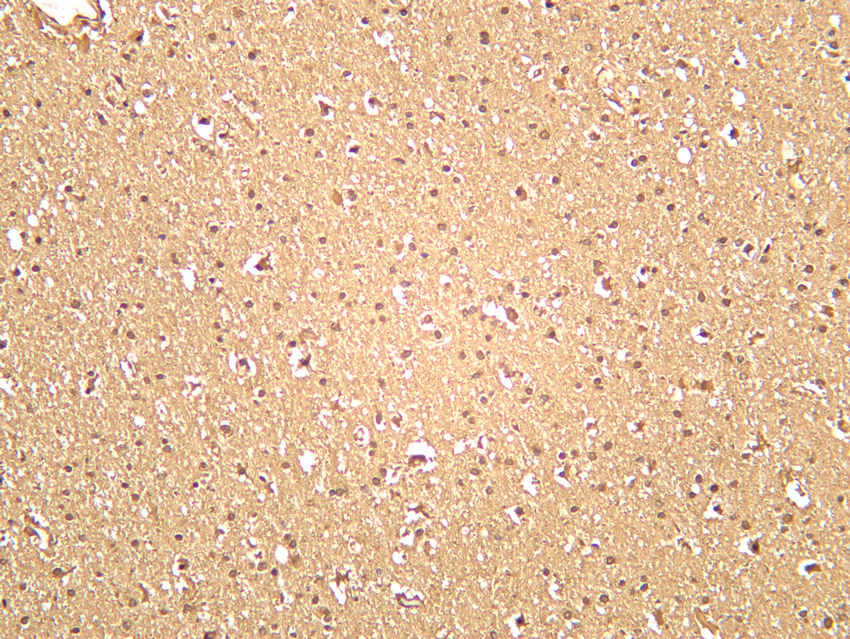
- Human brain was stained with anti-SOD1 (PT0113R) rabbit antibody
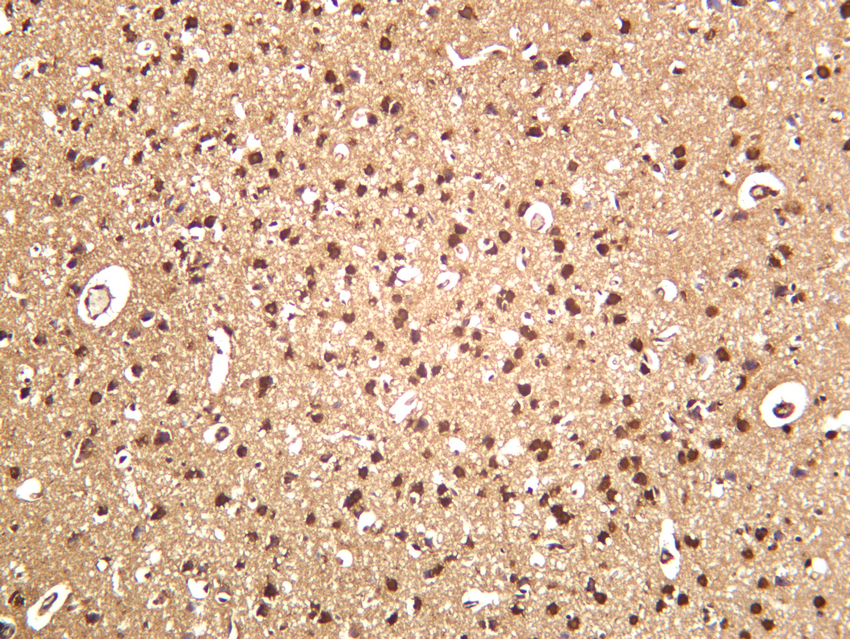
- Rat brain was stained with anti-SOD1 (PT0113R) rabbit antibody
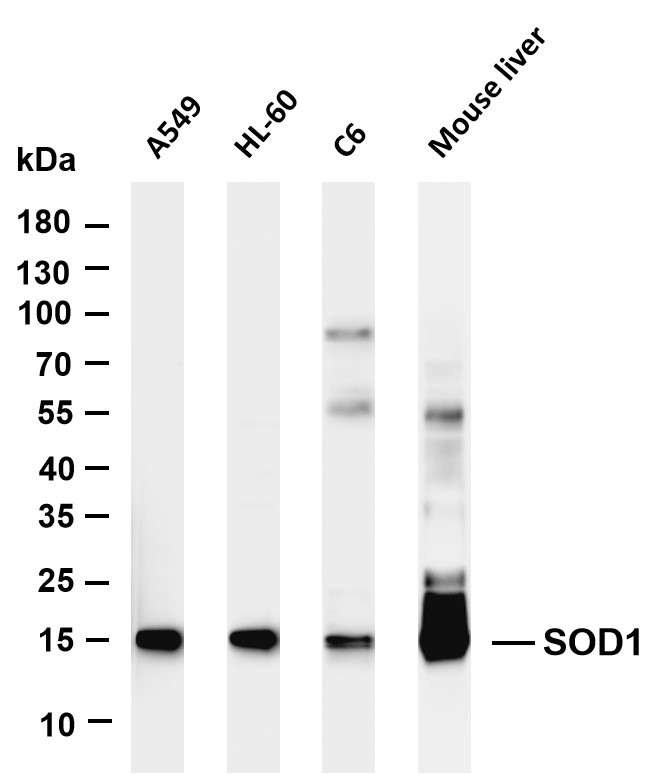
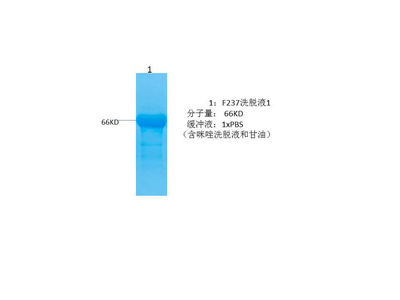
- Various whole cell lysates were separated by 4-20% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with anti-SOD1 (PT0113R) antibody. The HRP-conjugated Goat anti-Rabbit IgG(H + L) antibody was used to detect the antibody. Lane 1: A549 Lane 2: HL-60 Lane 3: C6 Lane 4: Mouse liver Predicted band size: 23kDa Observed band size: 15kDa