DPYD Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT5227
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- DPYD
- Fields:
- >>Pyrimidine metabolism;>>beta-Alanine metabolism;>>Pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis;>>Drug metabolism - other enzymes;>>Metabolic pathways
- Gene Name:
- DPYD
- Protein Name:
- Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase [NADP(+)]
- Human Gene Id:
- 1806
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q12882
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 99586
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q8CHR6
- Rat Gene Id:
- 81656
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- O89000
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human DPYD. AA range:351-400
- Specificity:
- DPYD Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of DPYD protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC: 1:100-300 ELISA: 1:20000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- DPYD;Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase [NADP(+)];DHPDHase;DPD;Dihydrothymine dehydrogenase;Dihydrouracil dehydrogenase
- Observed Band(KD):
- 120kD
- Background:
- The protein encoded by this gene is a pyrimidine catabolic enzyme and the initial and rate-limiting factor in the pathway of uracil and thymidine catabolism. Mutations in this gene result in dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency, an error in pyrimidine metabolism associated with thymine-uraciluria and an increased risk of toxicity in cancer patients receiving 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2009],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:5,6-dihydrouracil + NADP(+) = uracil + NADPH.,cofactor:Binds 2 4Fe-4S clusters. Contains approximately 33 iron atoms per molecule.,cofactor:Binds 2 FAD.,cofactor:Binds 2 FMN.,disease:Defects in DPYD are the cause of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency (DPYD deficiency) [MIM:274270]; also known as hereditary thymine-uraciluria or familial pyrimidinemia. DPYD deficiency is a disease characterized by persistent urinary excretion of excessive amounts of uracil, thymine and 5-hydroxymethyluracil. Patients suffering from this disease show a severe reaction to the anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil. This reaction includes stomatitis, Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, hair loss, diarrhea, fever, marked weight loss, cerebellar ataxia, and neurologic symptoms, progressing to semicoma.,function:Involved in pyrimidine base degradation. Catalyzes the reduction of uracil and thymine.
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm.
- Expression:
- Found in most tissues with greatest activity found in liver and peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
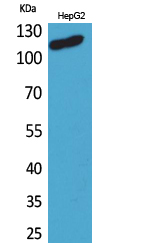
- Western Blot analysis of HepG2 cells using DPYD Polyclonal Antibody. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS0002) was diluted at 1:20000
.jpg)
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded mouse-lung, antibody was diluted at 1:100
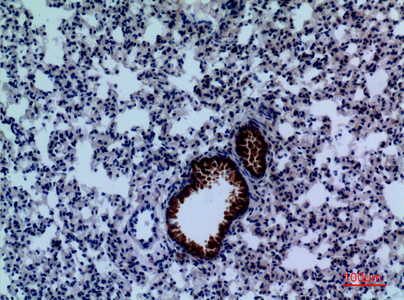
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded mouse-lung, antibody was diluted at 1:100
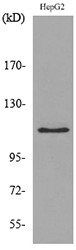
- Western blot analysis of lysate from HepG2 cells, using DPYD Antibody.



