Fibulin-4 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT1709
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Target:
- Fibulin-4
- Gene Name:
- EFEMP2
- Protein Name:
- EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 2
- Human Gene Id:
- 30008
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- O95967
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q9WVJ9
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human EFEMP2. AA range:91-140
- Specificity:
- Fibulin-4 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Fibulin-4 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- EFEMP2;FBLN4;EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 2;Fibulin-4;FIBL-4;Protein UPH1
- Observed Band(KD):
- 50kD
- Background:
- A large number of extracellular matrix proteins have been found to contain variations of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) domain and have been implicated in functions as diverse as blood coagulation, activation of complement and determination of cell fate during development. The protein encoded by this gene contains four EGF2 domains and six calcium-binding EGF2 domains. This gene is necessary for elastic fiber formation and connective tissue development. Defects in this gene are cause of an autosomal recessive cutis laxa syndrome. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2011],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in EFEMP2 are a cause of autosomal recessive cutis laxa type I (CL type I) [MIM:219100]. Hereditary cutis laxa refers to a heterogeneous group of connective tissue disorders characterized by cutaneous abnormalities and variable systemic manifestations. The most constant clinical feature is loose skin, sagging over the face and trunk. Hereditary cutis laxa is inherited in both autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive modes. CL type I shows the most severe phenotype and has the poorest prognosis. In addition to the skin, internal organs enriched in elastic fibers, such as the lung and arteries, are affected.,similarity:Belongs to the fibulin family.,similarity:Contains 6 EGF-like domains.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix . Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix, basement membrane . Localizes on the microfibrils surrounding ELN cores. .
- Expression:
- Brain,Melanoma,Placenta,Synovial membrane t
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
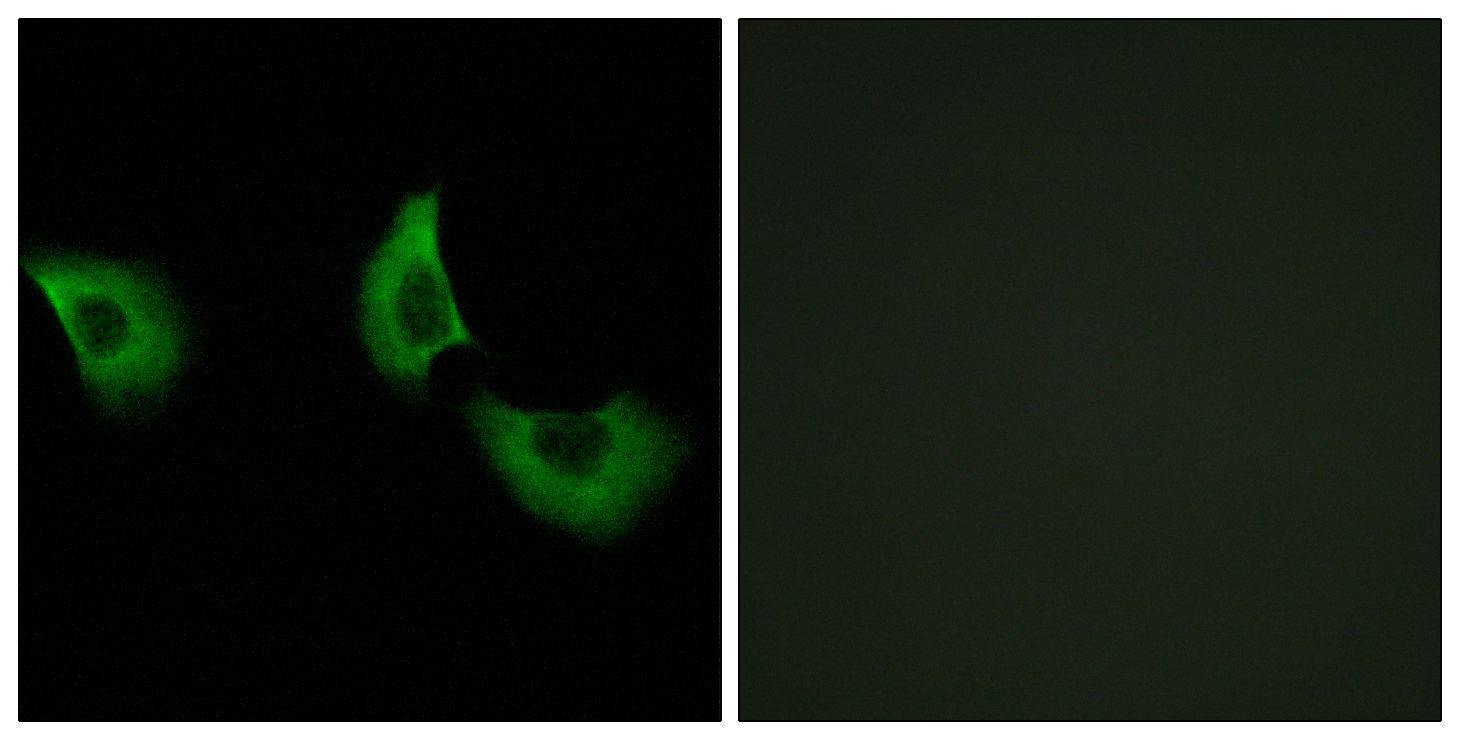
- Immunofluorescence analysis of A549 cells, using EFEMP2 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
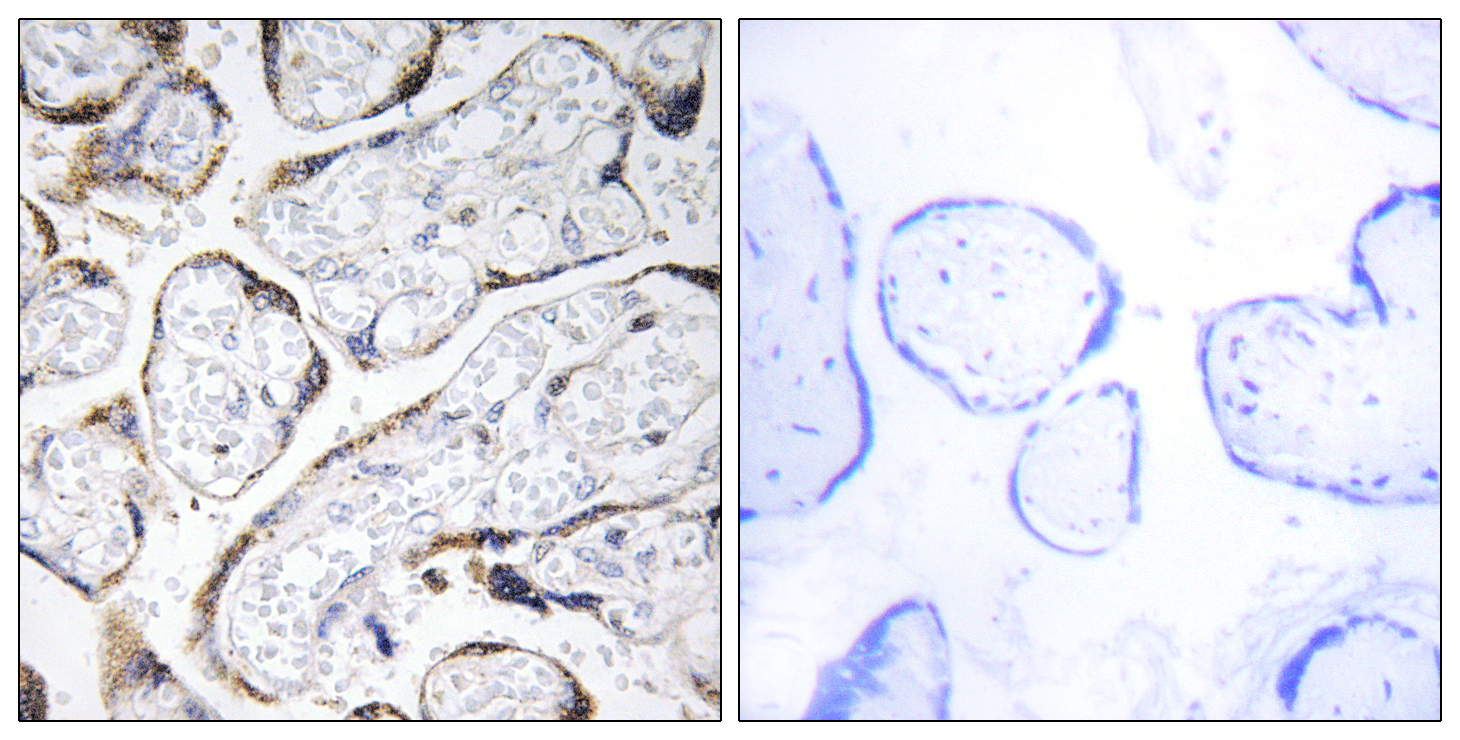
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human placenta tissue, using EFEMP2 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
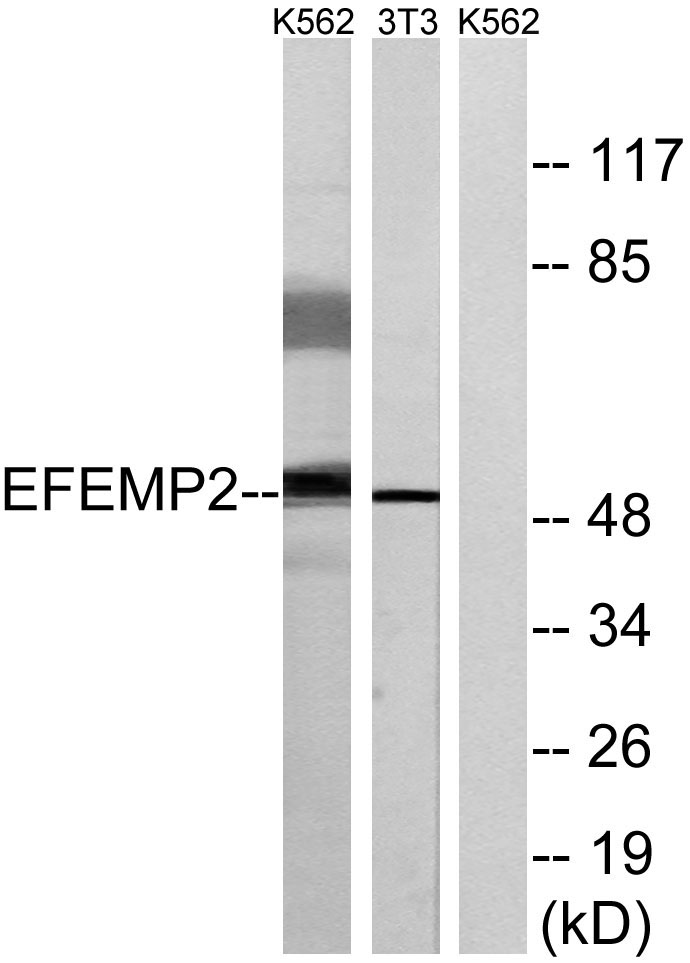
- Western blot analysis of lysates from K562 and NIH/3T3 cells, using EFEMP2 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.



